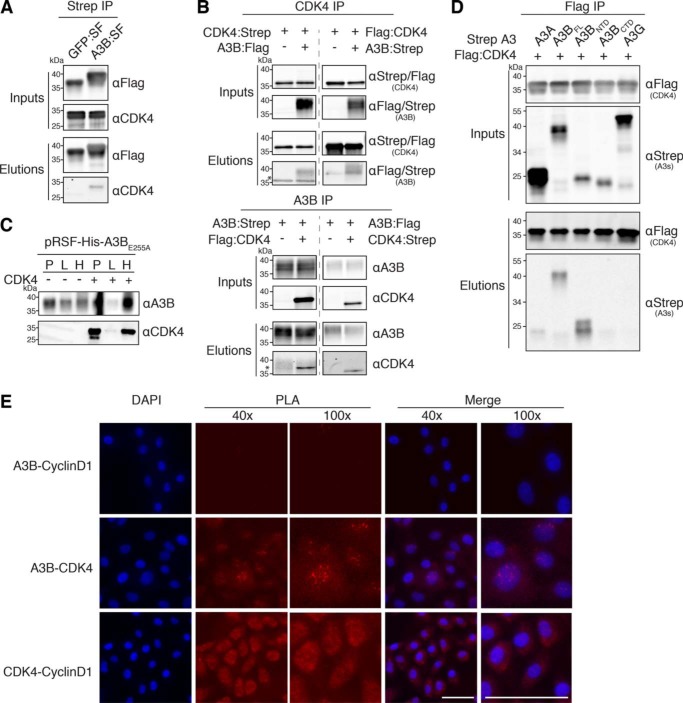
Figure 2.
Confirmation of the A3B–CDK4 interaction through IP experiments. A, co-IP of endogenous CDK4 in 293T cells transfected with A3B-SF. Parallel reactions with eGFP-SF serve as a negative control. Upper two immunoblots show the indicated proteins in whole cell lysates (input), and the bottom two immunoblots show the immunoprecipitated samples (elution). kDa markers are shown to the left of each blot and the primary antibody used for detection is shown to the right. B, co-IP results for Strep- and Flag-tagged CDK4 (upper blots) and Strep- and Flag-tagged A3B (bottom blots) from 293T cells. The asterisk denotes residual signal from the IP antibody due to insufficient stripping. C, immunoblots showing an interaction between E. coli expressed His-tagged A3BE255A and untagged CDK4. Immunoblot labels are as follows: insoluble pellet (P), lysate (L), and His purification (H). D, co-IP of the indicated Flag-tagged CDK4 constructs with Strep-tagged A3 constructs in 293T cells. E, fluorescence microscopy images of PLA results showing the interaction between A3B and CDK4 as well as CDK4 and Cyclin D1 in MCF10A cells treated with PMA to induce A3B expression (scale bar, 50 μm).