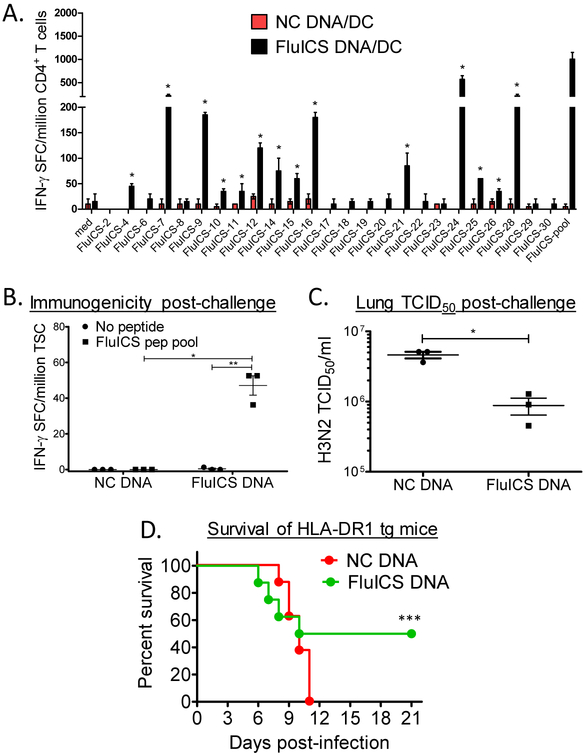
Figure 1. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of highly conserved class II immunogenic consensus sequences (ICS) in HLA-DR1 transgenic mice.
In panel A, female HLA-DR1 transgenic mice were vaccinated i.m. twice 2 weeks apart with a DNA vaccine encoding the 25 highly conserved influenza A ICS (FluICS) detailed in Table 1. These mice were additionally vaccinated with mature HLA-DR1 transgenic dendritic cells pulsed with these same epitopes. Shown are splenic CD4+ T cell IFN-γ ELISPOT responses determined 4 weeks after final vaccination, and 4 days post-intranasal A/PR/8 H1N1 (pooled cells from groups of N=2 mice; positive responses as defined in Methods marked with asterisks). In panels B-D HLA-DR1 transgenic mice were immunized 4 times with control or FluICS DNA vaccines. Four weeks post-vaccination mice were challenged intranasally with 30×LD50 Influenza A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2). Shown in panel B are total splenocyte IFN-γ ELISPOT results obtained 4 days post-challenge (N=3 female mice/group). Protection against H3N2 challenge was assessed 4 days post-infection by lung homogenate TCID50 assay (C; N=3 female mice/group) and by survival (D; N=8 mixed sex mice/group). (A-C) Data depicted as means ± standard errors. These data demonstrate that highly conserved influenza ICS are both immunogenic and protective in HLA-Tg mice. In panels B-D: *P<0.005 by 2-tailed unpaired t test, ** P=0.012 by 2-tailed paired t test, and ***P=0.039 by 1-tailed Fishers exact test.