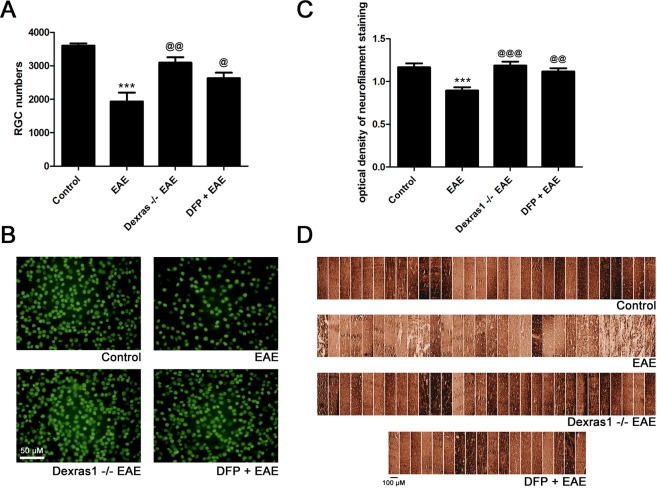
Figure 4.
Dexras1 deletion or iron chelation preserves RGC numbers in the retina and prevents axonal loss in the optic nerves of EAE mice. Neuroprotective effects of Dexras1 deletion or iron chelation were evaluated by counting RGCs in the retina and quantifying axonal staining density in the optic nerve. RGCs were immunolabeled with Brn3a antibody and counted in a standardized, masked fashion. (A) RGC loss in eyes of EAE mice (***p < 0.001 versus control, N = 5 right eyes of 5 mice) is reduced in Dexras1 KO EAE mice (@@p < 0.01 versus EAE, N = 5 eyes of 5 mice). Daily treatment with iron chelator DFP (1 mg/mL, N = 4 eyes of 4 mice) leads to significant (@p < 0.05 versus EAE) improvement in RGC numbers. (B) Representative images show RGCs in one field of retina from each group (original magnification ×20). (C) Neurofilament staining was used to evaluate axonal loss in sections of optic nerves isolated at day 42 post immunization. The optical density of neurofilament staining, calculated by a masked investigator using the average of three equal-sized fields from each optic nerve, shows a significant decrease (***p < 0.001) in optic nerves (N = 10 nerves) from EAE mice compared to optic nerves (N = 10 nerves) from control mice. Dexras1 KO EAE mice (@@@p < 0.001, N = 10 nerves) or DFP treated EAE mice (@@p < 0.01, N = 6 nerves) showed a significant increase in neurofilament staining compared to optic nerves from wild type EAE mice. (D) A series of photographs of axon staining in three equal-sized fields from each optic nerve (one each at the distal, central, and proximal regions of the longitudinal optic nerve section) shows the normal degree of variability of neurofilament staining in optic nerves of control mice. Similar staining is seen in Dexras1 KO EAE mice and EAE mice treated with DFP, whereas optic nerves from wild-type EAE mice show more patchy loss of neurofilament staining.