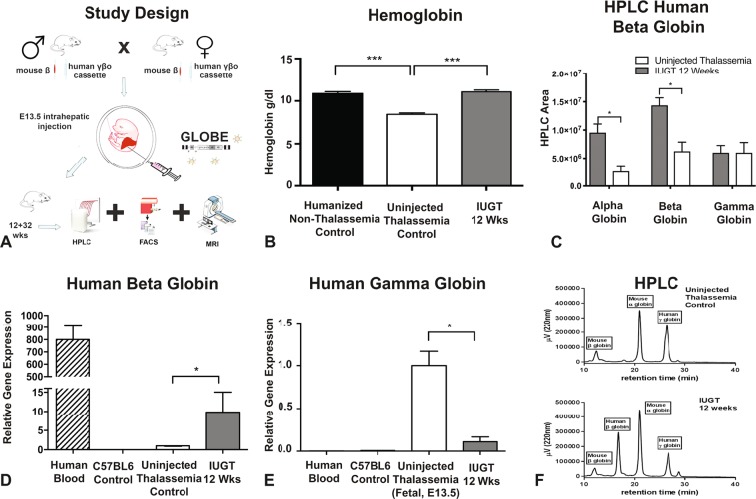
Figure 1.
Study Design and Phenotypic Correction at 12 Weeks. (A) Study design: Heterozygous males were mated with heterozygous females. At E13.5 in utero gene therapy was performed by injecting 20 μl of the GLOBE vector into the intrahepatic space of each fetus in the litter after exposure of the uterus at laparotomy. The dams were allowed to litter, and the pups were cross-fostered into CD1 time time-mated dams to avoid maternal antibodies towards the virus. Post-mortem and analysis were performed at 12 weeks in the first study and 32 weeks in the second. Any wild-type animals were excluded from analysis. (B) Measurement of Hemoglobin in Humanised Non-Thalassemia Control 11 ± 0.21 Versus Uninjected Thalassemia Control 8.4 ± 0.17 Versus IUGT 12 Weeks 11 ± 0.22, n = 8, ***p < 0.0001, One Way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s Multiple comparisons test. (C) Quantification of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography showing an increase of both alpha and beta globins (p = 0.0044) with the gamma globin remaining stable and similar between the two groups. (D) Real Time PCR of human beta globin relative gene expression showing upregulation of the beta-globin gene in the IUGT treated animals compared to untreated thalassemia controls. Wild-type C57BL6 and human blood were used as positive and negative primer controls, n = 10, p = 0.039, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, Two-stage linear step up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli. (E) Real Time PCR of human gamma-globin relative gene expression showing downregulation of the gamma-globin gene in the IUGT treated animals compared to untreated fetal thalassemia controls at E13.5, 0.11 ± 0.024 versus 1.0 ± 0, n = 10, p = 0.0002, ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, Two-stage linear step up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger and Yekutieli. Wild-type C57BL6 and human blood were used as negative primer controls. (F) Representative figure of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography showing the presence of a human beta globin chain pick in the IUGT group.