Figure 1.
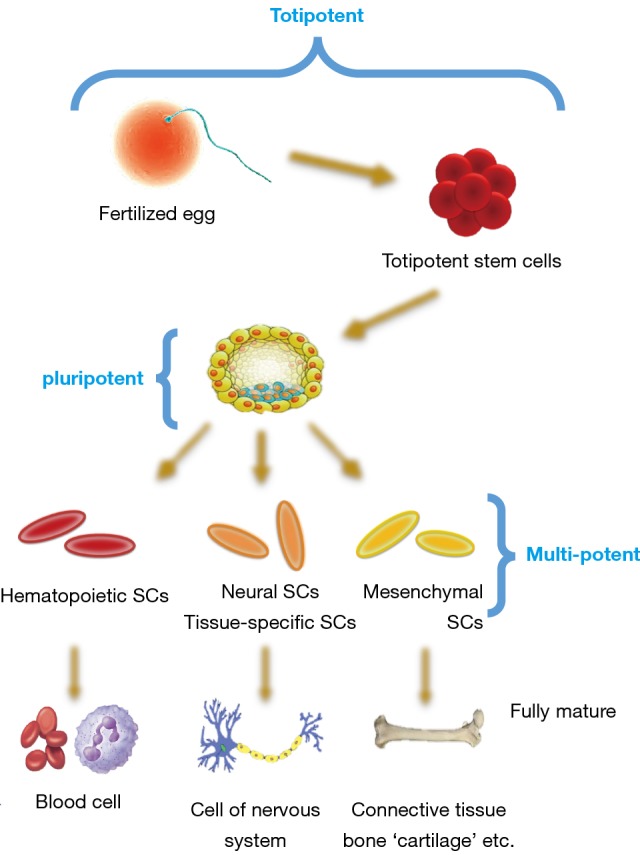
An overview of the stem cell classification. Totipotency: after fertilization, embryonic stem cells (ESCs) maintain the ability to form all three germ layers as well as extra-embryonic tissues or placental cells and are termed as totipotent. Pluripotency: these more specialized cells of the blastocyst stage maintain the ability to self-renew and differentiate into the three germ layers and down many lineages but do not form extra-embryonic tissues or placental cells. Multipotency: adult or somatic stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in postnatal tissues. These specialized cells are considered to be multipotent; with very limited ability to self-renew and are committed to lineage species.
