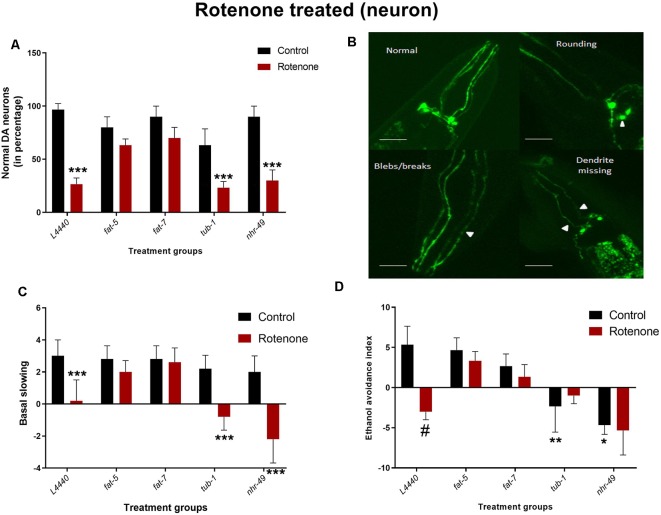
Figure 6.
Dopaminergic degeneration and related behaviors are rescued by silencing fat-5 and fat-7 genes in a rotenone-induced model of C. elegans. Graphical representation of (A) percentage of normal dopaminergic neurons (n = 25–30 animals per group). (B) Representative images of dopaminergic neurons with rounding neurons or axons with blebs or missing dendrite, any neurons having either of these morphological features were considered as not normal, magnification 40× and scale bar 50 μm.(C) Basal slowing and (D) ethanol avoidance behaviors (n = 10–15 animals) in TG2435 animals fed on different genetic RNAi treatments (L4440, fat-5, fat-7, nhr-49 and tub-1) and rotenone (0 and 4 μM). Empty vector L4440 was considered as control. The data represent the mean ± SEM with significant differences between the rotenone treated and untreated groups at #p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001. Each experiment was repeated three times.