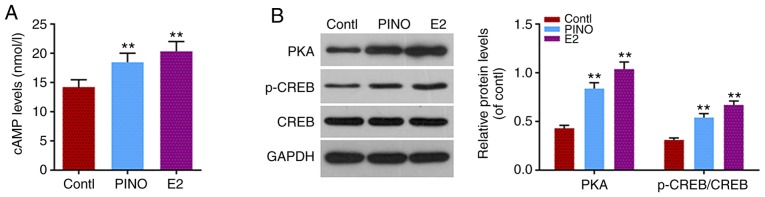
Figure 4.
The cAMP/PKA signaling pathway participates in the positive effects of PINO on osteoblastic differentiation. (A) In order to investigate the mechanism underlying the promoting effects of PINO on osteoblast differentiation, the cAMP level was detected by ELISA. (B) The activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway was reflected by the protein levels of PKA, CREB and p-CREB assessed by western blotting. Each value was represented by the mean ± SEM (n=3). GAPDH was used as an internal control. **P<0.01 vs. the control group. cAMP, cyclic AMP; PKA, protein kinase A; PINO, pinoresinol; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; p-CREB, phosphorylated CREB.