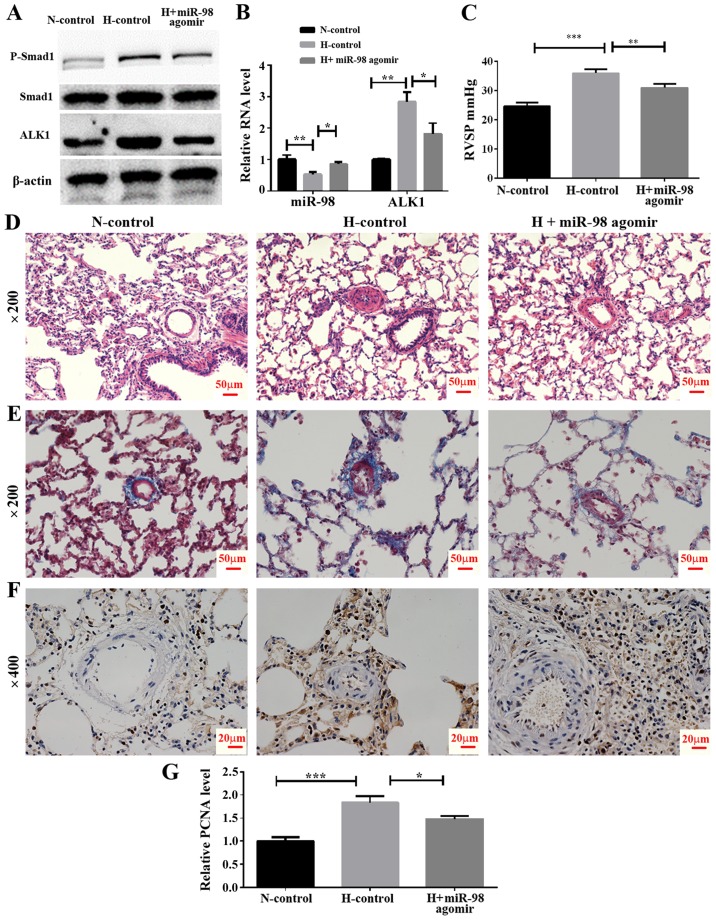
Figure 5.
Effect of miR-98 agomir treatment on hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction in the HPH rat model. (A) Western blot analysis of ALK1 and phosphorylated Smad1 levels in lung pulmonary arteries from normoxic and hypoxic rats with or without miR-98 agomir treatment. (B) Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of ALK1 and miR-98 expression in lung pulmonary arteries from N and H rats with or without miR-98 agomir treatment. (C) Measurement of RVSP. (D) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung pulmonary arteries (magnification, ×200). (E) Representative images of Masson staining of lung pulmonary arteries (magnification, ×200). (F) Representative immunohistochemical staining of PCNA in N-control, H-control and H + miR-98 agomir treatment groups (magnification, ×400). (G) Semi-quantitative analysis of immunohistochemical staining of PCNA (analyzed by ImageJ). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001. All experiments were repeated 3 times. miR, microRNA; HPH, hypoxic pulmonary hypertension; ALK1, activin receptor-like kinase-1; N, normoxia; H, hypoxia; RVSP, right ventricular systolic pressure; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; N-control, normoxic control group; H-control, hypoxia induced group; H + miR-98 agomir, hypoxia induced with miR-98 agomir.