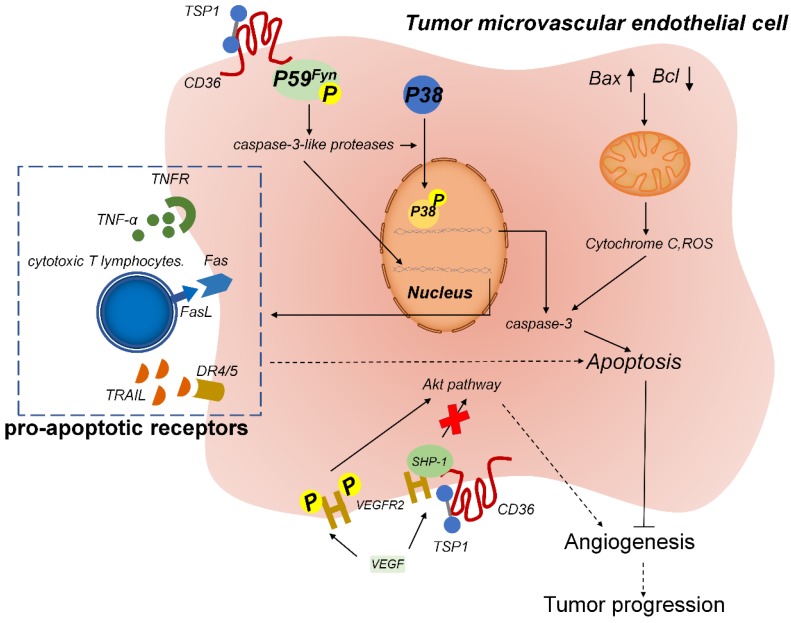
Figure 3.
TSP-1-CD36 signaling induces apoptosis of tumor-associated endothelial cells. TSP-1 binds to CD36 on microvascular endothelial cells and induces the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase P59fyn. Activated P59fyn stimulates caspase-3-like proteases, which activate and induce the phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Nuclear translocation of MAPK results in increased expression of caspase-3 and proapoptotic receptors, which leads to apoptosis. Furthermore, mitochondrial damage releases cytochrome C and reactive oxygen species (ROS), which also trigger the caspase-3 cascade to induce apoptosis. Moreover, TSP-1 biding to CD36 results in the recruitment of Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1 to the VEGFR2 complex and SHP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of VEGFR2, which inhibits the VEGF pathway and thus leads to anti-angiogenesis.