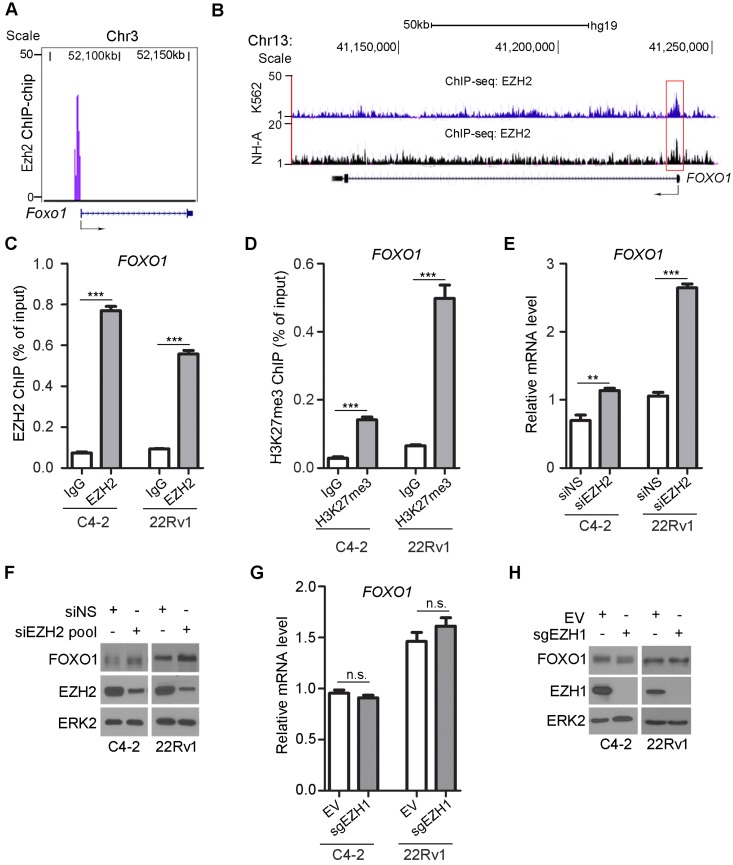
Figure 1.
FOXO1 gene is a repression target of EZH2. (A) EZH2 ChIP-on-chip assay reveals murine Ezh2 binds to the Foxo1 promoter in mouse embryo stem cells. (B) Screen shot of the UCSC genome browser showing ChIP-seq (reported previously 43, 44) signal profiles of EZH2 binding in the FOXO1 gene locus in different human cell lines. (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of EZH2 occupancy in the FOXO1 promoter in both C4-2 and 22Rv1 prostate cancer cell lines. (D) ChIP-qPCR analysis of H3K27me3 enrichment in the FOXO1 promoter in prostate cancer cell line C4-2 and 22Rv1 cells. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of FOXO1 mRNA expression in C4-2 and 22Rv1 cells transfected with non-specific (NS) control or a pool of EZH2-specific siRNA for 48 h. RT-PCR for GAPDH was utilized as an internal control. (F) Western blot analysis of FOXO1 and EZH2 proteins in C4-2 and 22Rv1cells transfected with non-specific (NS) control or a pool of EZH2-specific siRNA for 48 h. ERK2 was used as a loading control. (G, H) RT-qPCR (G) and western blot (H) analysis of FOXO1 mRNA and protein expression in C4-2 and 22Rv1 cells transfected with empty vector or EZH1-specific sgRNA and selected with puromycin for one week. RT-qPCR for GAPDH was utilized as an internal control. Data are shown as means ± SEM. The P value was performed by the unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001; n.s., no significance.