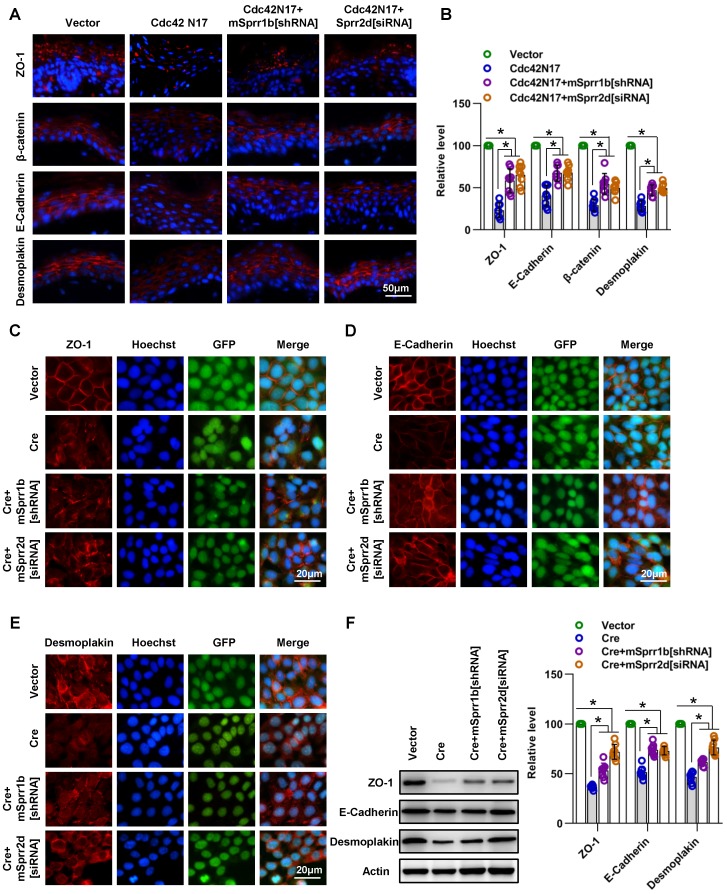
Figure 9.
SPRR1B and SPRR2D are partially responsible for altered intercellular junctions and skin barrier dysfunction resulting from Cdc42 suppression. (A) The lentiviral vectors Cdc42N17 were applied to the skin of C57BL/6 mice. The mouse skin was transfected with Cdc42N17 and mSprr1b[shRNA] vectors at the same time. For the Cdc42N17+mSprr2d[siRNA] group, the skin was transfected with mSprr2d[siRNA] for 3 days and then infected with Cdc42N17 vectors for another 3 days. The expression and distribution of ZO-1, β-catenin, E-cadherin and desmoplakin were determined by immunohistochemistry. (B) Immunofluorescent semiquantification of ZO-1, β-catenin, E-cadherin and desmoplakin. n = 8, *p<0.05. Primary keratinocytes were isolated from P1 Cdc42loxp/loxp/Cre- mice and then infected with vector or plenti-Cre; in the plenti-Cre+mSprr1b[shRNA] group, keratinocytes were infected with plenti-Cre and mSprr1b[shRNA] vectors; in the plenti-Cre+ mSprr2d[siRNA] group, keratinocytes were infected with plenti-Cre and then treated with mSprr2d[siRNA]. The cells were grown to confluence in low-calcium medium for 24 hours and then incubated in high-calcium medium for 12 h. Cells were stained for ZO-1 (C), E-cadherin (D) and desmoplakin (E). (F) Vector-infected keratinocytes, plenti-Cre-infected keratinocytes, plenti-Cre+ mSprr1b[shRNA] keratinocytes, and plenti-Cre+ mSprr2d[siRNA] keratinocytes were grown in low-calcium medium, and WB of cell lysates was performed with anti-ZO-1, E-cadherin and desmoplakin antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control. The experiments were repeated at least eight times; *p<0.05.