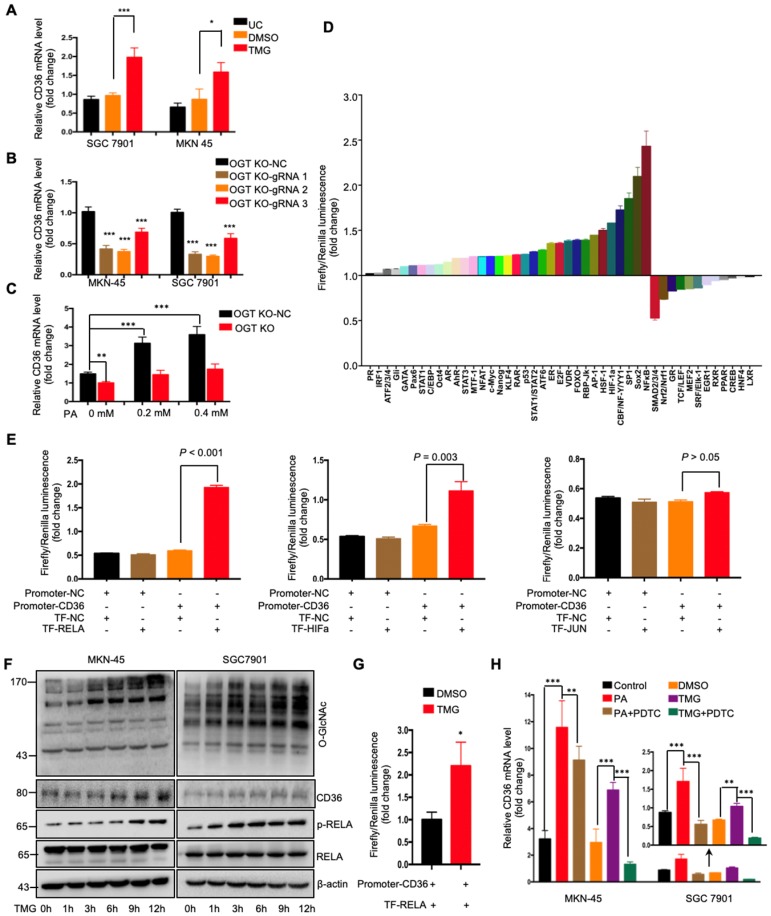
Figure 5.
O-GlcNAcylation promoted CD36 transcription via activating the NF-κB pathway. (A) CD36 mRNA levels in MKN-45 or SGC 7901 cells were assessed by real-time PCR after a 24-hour treatment with TMG (10 μM) or isometric DMSO. (B) CD36 mRNA levels were assessed in MKN-45 or SGC 7901 OGT-knockout cells by real-time PCR. (C) CD36 mRNA levels in SGC 7901 cells with or without OGT knockout after treatment with the indicated concentration of PA for 24 h. (D) A luciferase reporter assay showed changes in the activity of 45 signal transduction pathways in SGC 7901 cells after a 24-hour treatment with TMG (10 μM). (E) A luciferase reporter assay showed the regulation of CD36 transcription by the indicated transcription factors in HEK 293T cells. (F) The levels of O-GlcNAcylation, RELA, phosphorylated RELA and CD36 in MKN-45 or SGC 7901 cells were assessed by western blotting after treatment with 10 μM TMG or isometric DMSO for the indicated times. β-actin was used as a loading control. (G) A luciferase reporter assay showed the regulation of CD36 transcription by NF-κB after treatment with 10 μM TMG or isometric DMSO for 12 h. (H) CD36 mRNA levels in MKN-45 or SGC 7901 cells were assessed by real-time PCR after the indicated treatment. The values shown are expressed as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. Control: control solvent treatment for 24 h; PA: treatment with 0.4 μM of PA for 24 h; PA+PDTC: treatment with 0.4 μM of PA for 24 h and pretreatment with 50 µmol of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for 4 h; DMSO: isometric DMSO treatment for 24 h; TMG: treatment with 10 μM of TMG for 24 h; TMG+PDTC: treatment with 10 μM of TMG for 24 h and pretreatment with 50 µmol of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for 4 h.