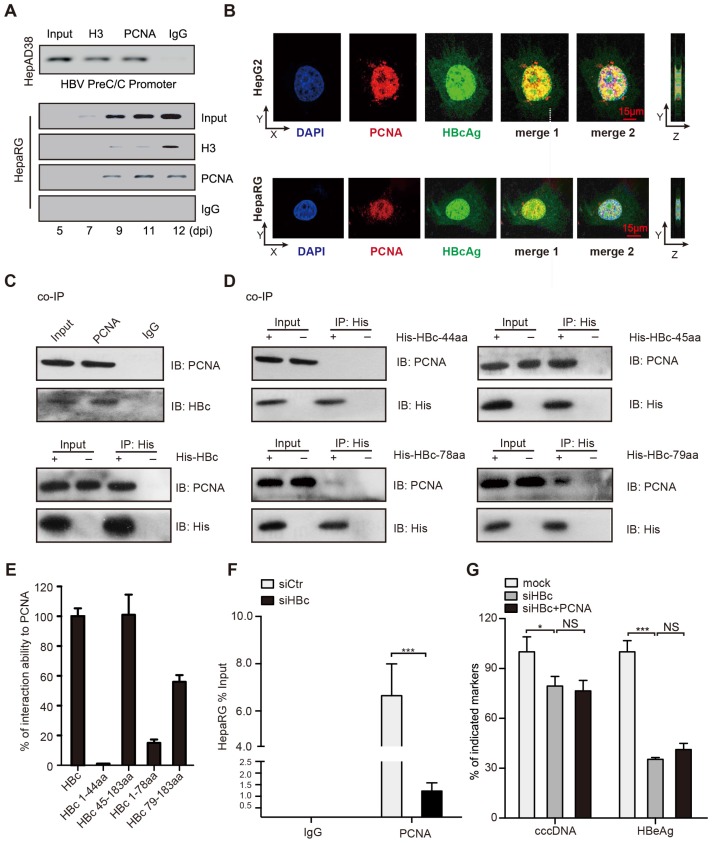
Figure 3.
PCNA anchors onto cccDNA minichromosome through interacting with HBc. (A) Upper: cross-linked chromatin from HepAD38 cells treated without tetracycline was immunoprecipitated and analyzed by PCR. Bottom: kinetics of histone H3 and PCNA recruitment onto the HBV cccDNA in infected HepaRG cells. (B) In HepG2 cells transfected with PCH9/3091 plasmids and HBV-infected HepaRG cells, the colocalization of PCNA and HBc was analyzed by immunofluorescence. Right panels indicate Z stacks taken at the dotted lines. (C) Upper: the interaction between PCNA and HBc was identified in HepG2.2.15 cells. Bottom: in HepG2 cells cotransfected with PCH9/3091 plasmids and His-HBc, the interaction between PCNA and HBc was identified by co-IP assays. (D and E) Serial HBc deletion mutants were fused to His protein and interaction with PCNA was assessed by co-IP assays in HepG2 cells. (F) HepaRG cells were infected with HBV particles and transfected with siCtr or siHBc. The levels of cccDNA were analyzed by ChIP-qPCR. (G) HBV indicated markers including cccDNA and HBeAg were measured as above in HepG2.2.15. Error bars represent means ± SD (n=3). Statistical significant differences are indicated: ***P<0.001; NS, no significance; Student's t test.