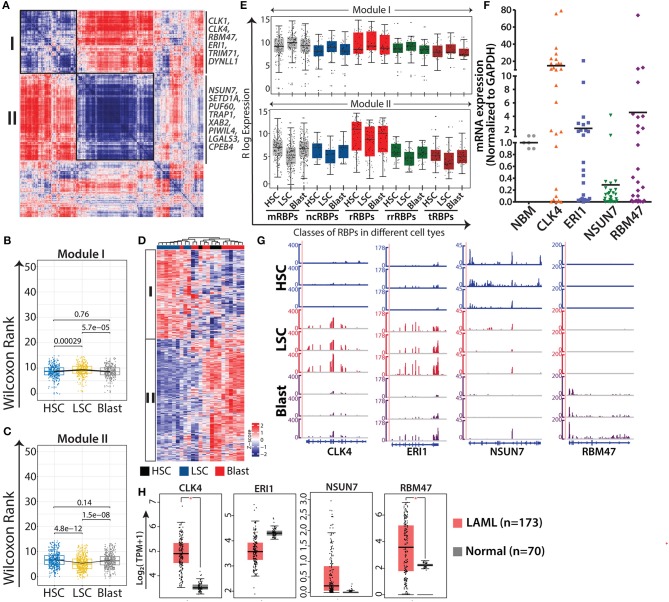
Figure 4.
AML specific modules obtained from gene-gene correlation studies. Heat map showing Spearman correlation plot based on RBP gene expression values, and the black boxes show two major modules that were considered for further studies (A). Box-whisker plots represent overall gene expression patterns of RBPs in HSC, LSC, and blasts across two modules Wilcoxon rank test shows p-values for each comparisons (B,C). Unsupervised clustering of RBP gene expression in different modules (D). Box-whisker plots showing expression of different classes of RBPs in module I (left) and module II (right); p-values for comparing the difference in each RBP class for different cell types is listed in Supplementary Table 7 (E). qRT-PCR validations of the expression of selected RBPs, CLK4 (p = 0.0018), ERI1 (p = 0.1892), NSUN7 (p = 0.0001), and RBM47 (p = 0.1869) in samples from AML patients together with age-matched normal samples as controls (F). Genome browser plots of CLK4, ERI1, NSUN7, and RBM47 in individual samples of HSC, LSC, and blasts (G). Box-whisker plot depicting the expression profiles of the same genes (H) in AML cohorts of TCGA and GTEx visualized in a GEPIA2 platform using default parameters (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.01). *p < 0.01.