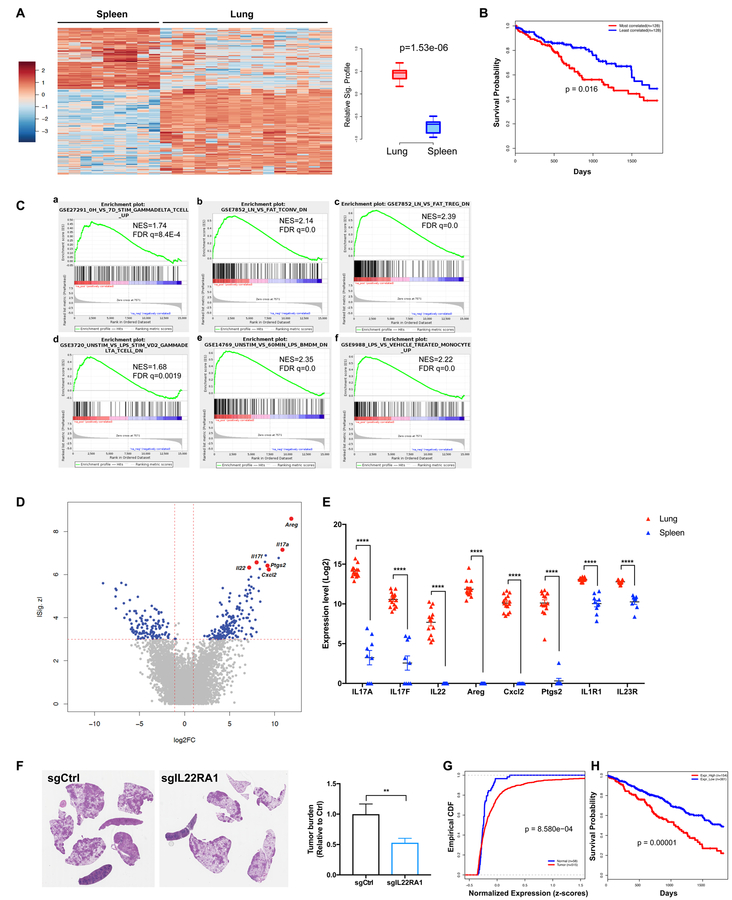
Figure 7. γδ T cells associated with lung tumors exhibit a distinct transcriptional profile.
(A–E) γδ T cells were FACS purified from tumor-bearing lungs or spleens of KP mice and their gene expression was analyzed by RNA-seq. A total of 9 spleen and 15 lung samples from three independent experiments were sequenced.
(A) Heatmap showing differential expression of driver genes of the KP-lung versus spleen γδ T signature (|Z| > 3, fold change > 2). Boxplot illustrating the significant difference between standardized signature scores of sample groups.
(B) Kaplan-Meier (KM) survival curves comparing subjects in the TCGA LUAD cohort stratified by correlation with the mouse-derived KP-lung γδ T signature. The top 25% most correlated patients (n = 128, red) exhibited significantly decreased survival as compared to the 25% least-correlated patients (n = 128, blue) from the TCGA LUAD cohort (p=0.016, log-rank test).
(C) Relevant gene set enrichment plots from GSEA of the KP lung γδ T signature (NES: Normalized Enrichment Score; FDR: False discovery rate).
(D) Volcano plot illustrating the magnitude of fold-change (x-axis, lung/spleen log2 fold change) for all genes ranked by their absolute z-score in the KP lung γδ T signature (y-axis). Some of the driver genes highly-upregulated in lung samples are highlighted.
(E) Pairwise comparison of the expression levels of 8 relevant genes between KP-lung and spleen samples (**** denotes FDR<1.63E-12).
(F) KP-R26LSL-cas9 mice were infected with lentiviral vectors co-expressing Cre and sgRNA against IL-22RA1 or an irrelevant locus (control). Tumor burden was quantified at 10 weeks post tumor initiation and representative H&E pictures are shown.
(G) Empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) plots showing expression of IL22RA1 in human LUAD samples (n=515) in comparison to normal lung tissues (n=58) from the TCGA cohort (p = 8.58E-04, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test).
(H) KM survival curves comparing subjects in the TCGA LUAD cohort stratified by IL22RA1 expression. The patients with high IL22RA1 expression (top 30%) exhibit significantly worse survival when compared to the rest of the patients in the cohort (p=0.00001, log-rank test).
See also Figure S7.