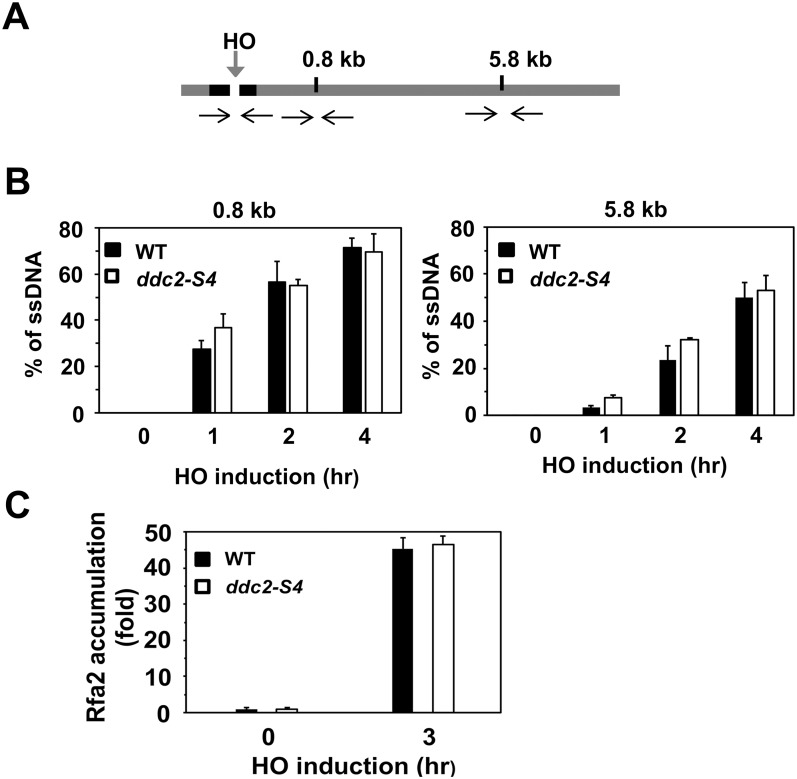
Fig 2. Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on DNA end resection and RPA accumulation.
(A) Scheme of the ADH4 locus containing a HO cleavage site. One EcoRI restriction site is located 0.8 kb away from the HO cleavage site whereas another is 5.8 kb away. The black arrows indicate PCR primer pairs to monitor HO or EcoRI cleavage. (B) Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on DNA end resection. Wild-type (HB01) or ddc2-S4 (HB02) cells carrying YCpA-GAL-HO were grown in sucrose and treated with nocodazole. After arrest at G2/M, the culture was incubated with galactose to induce HO expression. Cells were collected at the indicated times for genomic DNA preparation. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and analyzed by real-time PCR. Experiments were carried out three times. The error bars indicate standard deviation. (C) Effect of ddc2-S4 on Rfa2 localization to a HO-induced DSB. Wild-type (HB01) or ddc2-S4 (HB02) cells were transformed with the YCpA-GAL-HO plasmid. Transformed cells were grown in sucrose and treated with nocodazole. The culture was then incubated with galactose for 3 hr to induce HO expression, while half of the culture was maintained in sucrose to repress HO expression. Cells were subjected to chromatin immunoprecipitation with anti-Rfa2 antibodies. Association of Rfa2 with a HO-induced DSB was analyzed by real-time PCR. Relative enrichment was determined from three independent experiments. The error bars indicate standard deviation.