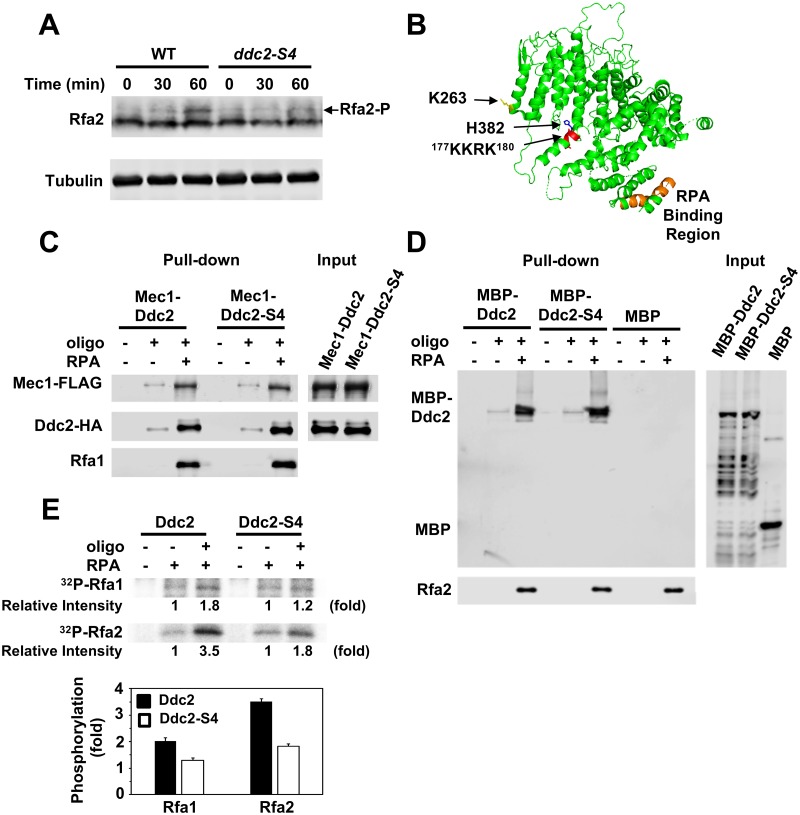
Fig 5. Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on RPA phosphorylation in vivo and in vitro.
(A) Rfa2 phosphorylation after exposure to MMS. Wild-type (HB01) or ddc2-S4 (HB02) cells were cultured as in Fig 1A and subjected to immunoblotting analysis with anti-Rfa2 antibodies. (B) Position of the ddc2-S4 substitution mutation sites. The putative DNA binding (177KKRK180) and the RPA binding (amino acid 10 to 30) [64] region are highlighted in red and orange, respectively. The side chain of K263 and H382 residues is shown in yellow and blue, respectively. (C) Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on ssDNA-binding of Mec1-Ddc2. Streptavidin beads were first incubated with RPA (1 pmol) or bio-oligo(dN)80 (5 pmol). Beads were further incubated with Mec1-Ddc2 or Mec1-Ddc2-S4 (0.5 pmol). Captured proteins on beads were detected by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, anti-HA or anti-Rfa1 antibodies. Note that Mec1 is FLAG-tagged and Ddc2 is HA-tagged. (D) Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on ssDNA-binding of Ddc2. Streptavidin beads were first incubated with RPA (1 pmol) or bio-oligo(dN)80 (5 pmol). Beads were further incubated with MBP, MBP-Ddc2 or MBP-Ddc2-S4 (0.5 pmol). MBP or MBP-fusion proteins were prepared from E. coli. Captured proteins on beads were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-MBP or anti-Rfa2 antibodies. (E) Effect of ddc2-S4 mutation on RPA phosphorylation in vitro. Kinase reactions were carried out with Mec1-Ddc2 or Mec1-Ddc2-S4 (5 nM) in the absence or the presence of RPA (10 nM) or bio-oligo(dN)80 (125 nM). Incorporation of 32P into Rfa1 and Rfa2 were normalized to that observed with Rfa1 and Rfa2 alone. The error bars indicate standard deviation from three independent experiments.