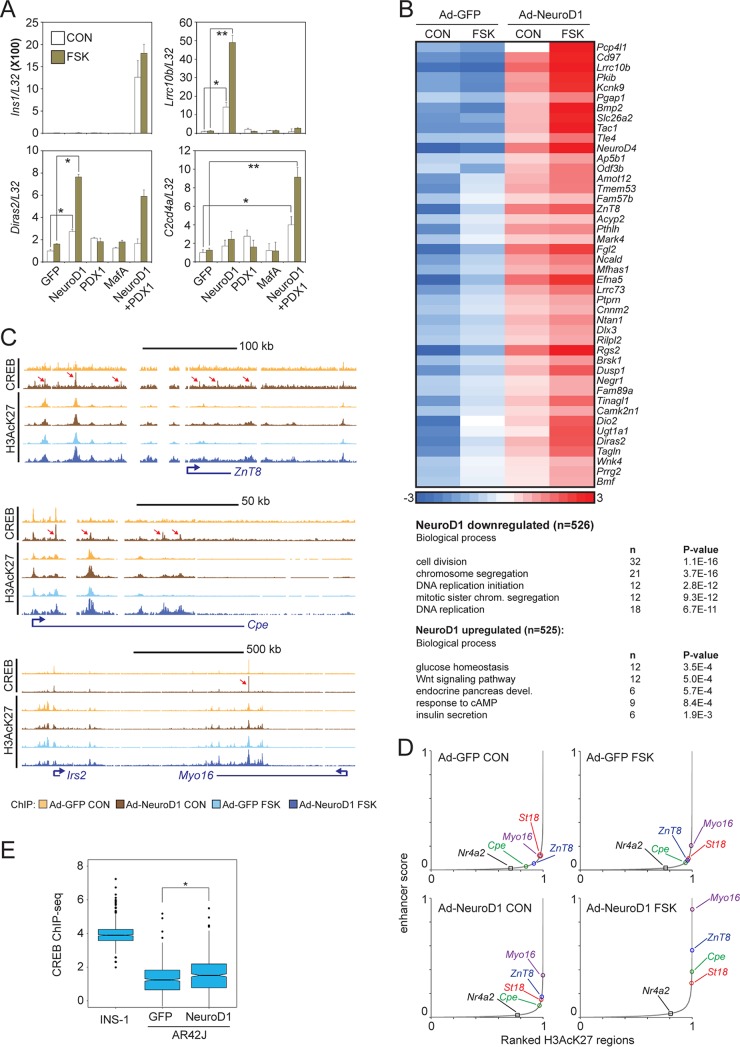
FIG 6.
Neurod1 promotes CREB occupancy at binding sites within beta cell-specific enhancers. (A) Effect of beta cell transcription factor (Pdx1, Neurod1, and MafA) overexpression on mRNA amounts for beta cell-restricted CREB targets Lrrc10b, Diras2, and C2cd4a in AR42J pancreatic exocrine cells. *, P < 0.02; **, P < 0.005. Ins1 expression is shown. Exposure to FSK (green) or vehicle (white) is indicated. (B) Heat map showing effect of adenoviral Neurod1 on cAMP-inducible gene expression in pancreatic exocrine AR42J cells. (Top) AR42J cells were treated with FSK for 2 h. Heat map depicts RNA-seq data of a cluster of Neurod1- and FSK-induced genes. (Bottom) Enrichment in biological process of NeuroD1-induced and repressed genes. (C, top tracks) Browser plots showing effect of adenoviral NeuroD1 expression on CREB occupancy over beta cell-specific loci. (Bottom tracks) Effect of FSK on enhancer activation (H3AcK27 occupancy) over beta cell-specific gene loci. AR42J cells were treated with FSK for 1 h. Arrows point to induced CREB-bound loci. (D) Effect of Neurod1 expression and FSK treatment alone or together on beta cell-specific enhancer strength. AR42J cells infected with control (GFP) or Neurod1-expressing adenovirus and treated with FSK for 1 h. (E) Box plot showing genome-wide enrichment of CREB binding over INS-1-specific CREB-bound loci following adenoviral Neurod1 expression in AR42J cells. INS-1-specific CREB binding loci are defined as regions with a ≥4× enrichment of CREB tags in INS-1 cells relative to that in AR42J cells. *, P < 2 × 10−9.