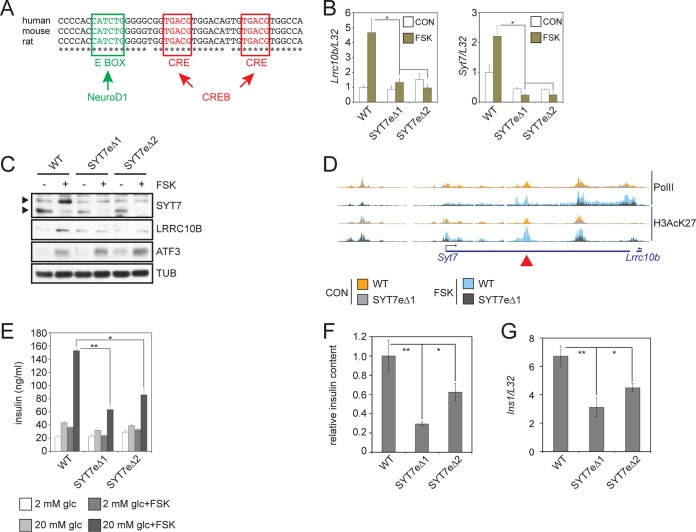
FIG 7.
Conserved CREB-Neurod1-regulated superenhancer is required for insulin secretion. (A) Conservation of E-box and CRE sites within the Syt7 enhancer in human, mouse, and rat. (B) Relative effect of FSK on mRNA amounts for Lrrc10b and Syt7 in wild-type and enhancer-deleted SYT7eΔ lines. *, P < 0.02. Two immunoreactive Syt7 bands represent phospho (top) and dephospho (bottom) forms of Syt7. (C) Immunoblot showing effect of FSK on protein amounts for Lrrc10B and Syt7 in wild-type and SYT7eΔ lines. Cells were exposed to 10 μM FSK for 8 h. ATF3 included as a control for CREB target protein induction. Exposure to FSK reduces Syt7 mobility due to PKA-mediated phosphorylation. Arrows indicate phospho- and unphospho-Syt7. (D) Browser plot showing relative Pol II and H3AcK27 occupancy over the Lrrc10b/Syt7 enhancer in wild-type and SYT7eΔ1 mutant cells. Exposure to FSK (10 μM, 1 h) is shown. The location of deleted enhancer is indicated with an arrowhead (top). (E) Signal-induced insulin secretion assay in wild-type and SYT7eΔ lines. Cells were exposed for 2 h to glucose (glc) and FSK as indicated. Insulin secretion measured in KRBH buffer by radioimmunoassay. *, P < 0.003; **, P < 2 × 10−4. (F) Relative content of mature insulin in extract from wild-type and SYT7eΔ lines measured by radioimmunoassay. *, P < 0.04; **, P < 0.02. (G) Ins1 mRNA levels in wild-type and SYT7eΔ lines. *, P < 0.005. **, P < 0.0004.