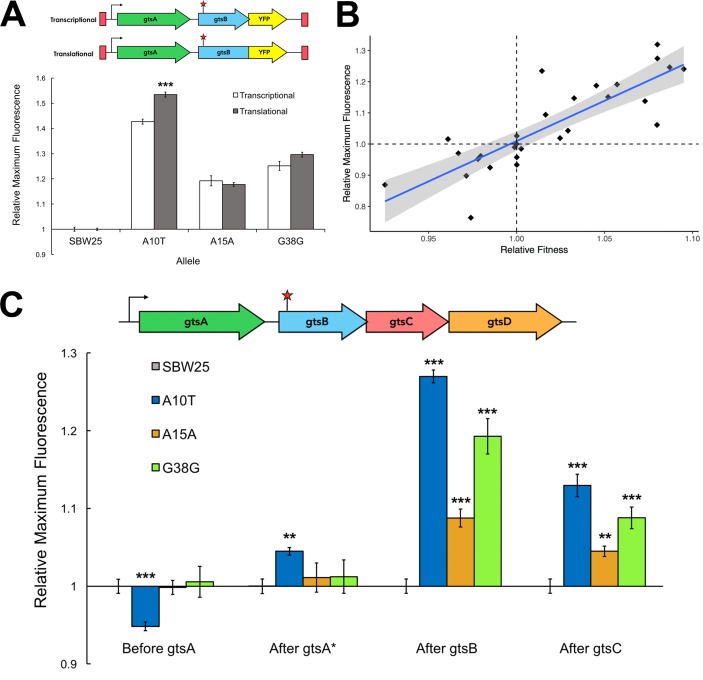
Figure 2. Comparison of transcriptional and translational effects of the evolved mutants and correlation with relative fitness.
(A) The schematic shows the sites of YFP insertion for transcriptional and translational fusions. The plot compares maximum YFP expression (± SEM) from transcriptional and translational YFP fusions at the Tn7 site for the WT (n = 14 replicates) and evolved mutants (n = 7, 7, and six technical replicates, respectively). Significance with respect to transcriptional fusion: ***p<0.001. See Figure 2—source data 1. (B) Linear regression of fluorescent signal of YFP transcriptional fusions as a proxy for transcript levels and relative fitness measures for a subset of synonymous mutations (n = 27). Grey shading indicates the 95% confidence interval for the regression (adjusted R2 = 0.69, p<0.001). See Figure 2—source data 2. (C) Expression of transcriptional YFP fusions inserted across the gts operon of evolved mutants. Maximum fluorescence (± SEM) of the YFP transcriptional fusions at different loci in the gts operon relative to SBW25. See Figure 2—source data 3; YFP fusion positions are depicted in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.