Figure 5:
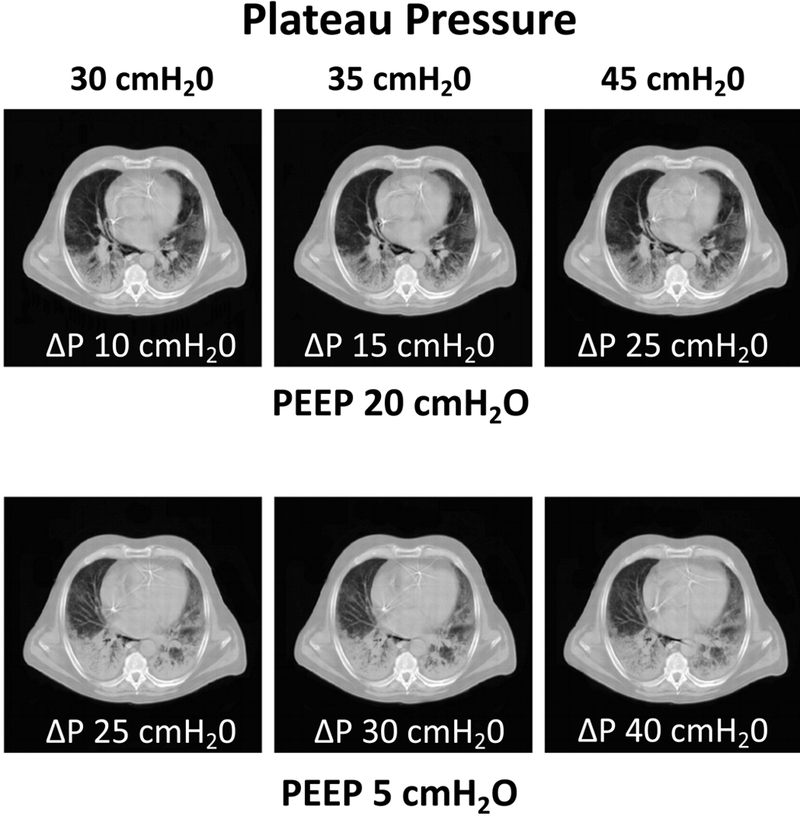
End-expiratory CT scans obtained in a patient with ARDS at high PEEP (20 cmH2O, Panel A) and low PEEP (5 cmH2O, Panel B). In each panel, three values of inspiratory plateau pressure (Pplat 30, 35 and 45 cmH2O) are targeted, and in each case the resultant driving pressure (ΔP = Pplat - PEEP) is indicated below each image. For each Pplat, atelectasis was more pronounced when the PEEP was lower, irrespective of the inspiratory ΔP. The CT illustrates that alveolar recruitment achieved by high inflation pressure is not maintained during expiration unless stabilized by sufficient PEEP. Reproduced with permission, Ref. 110.
