Figure 1. Neuroprotective mechanisms of sleep.
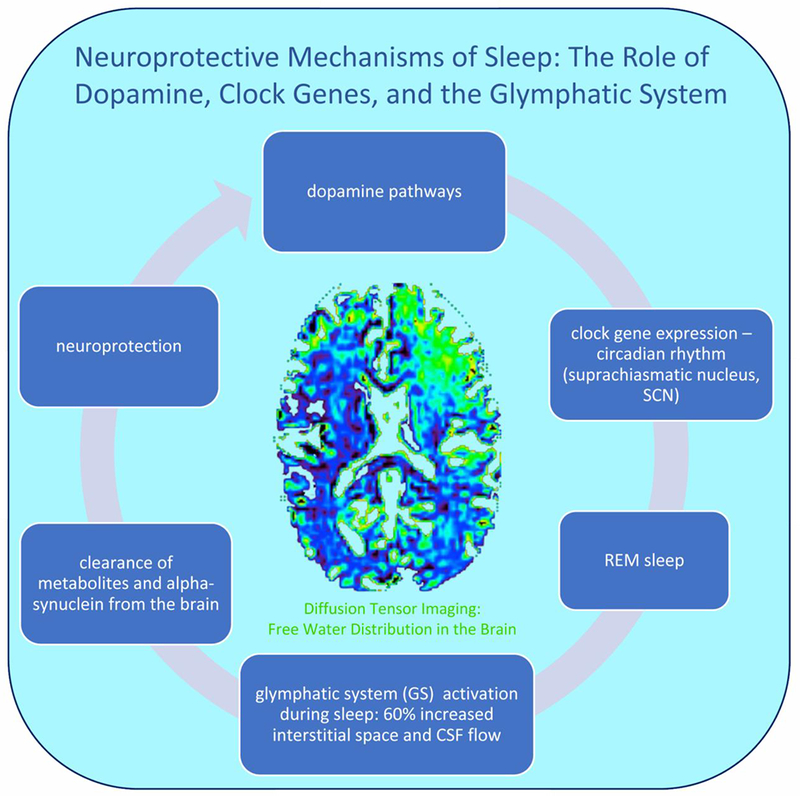
Midbrain dopamine neurons innervate corticolimbic and nigrostriatal systems involved in the control of sleep and wake states, including the SCN (circadian rhythm) (Monti and Monti, 2007) and striatal clock gene expression (Verwey et al., 2016) that promote healthy sleep. During sleep, glymphatic system activity is characterized by a 60% increase in the interstitial space and CSF flow (Jessen et al., 2015; Xie et al., 2013), and clearance of alpha-synuclein, along with other protein accumulations, from the brain (Iliff et al., 2012). Non-invasive free-water diffusion tensor imaging (FW-DTI) can be utilized in human subjects to detect the percent of free water in the tissue during sleep and wake states (Thomas et al., 2018).
