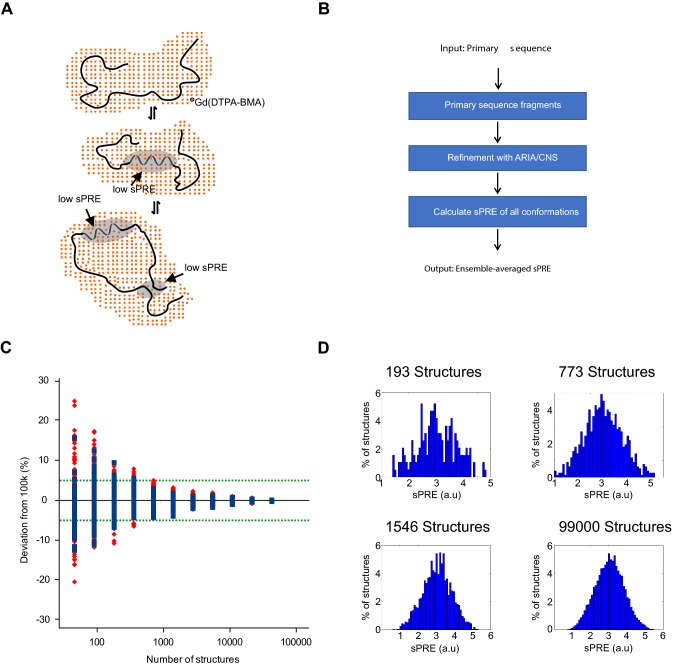
Fig. 1.
Principle and workflow for solvent PRE. a Transient secondary structures of IDPs are characteristic for protein–protein interaction sites and are therefore crucial for various cellular functions. NMR sPRE data provide quantitative and residue specific information on the solvent accessibility as the effect of paramagnetic probes such as Gd(DTPA-BMA) is distance dependent, which can be used to detect secondary structures within otherwise unfolded regions and long-range contacts within a protein. b Prediction of sPRE is based on an ensemble approach of a library of peptides. Each peptide has a length of 5 residues, and is flanked by triple-Ala on both termini (e.g. AAAXXXXXAAA, where XXXXX is a 5-mer fragment of the target primary sequence). Following water refinement using ARIA/CNS, sPRE values of all conformations are calculated and the average solvent PRE value of the ensemble is returned. c Predicted Cα sPRE (blue) and standard deviation (red) of AAAVVAVVAAA ensembles consisting of 99,000 down to 48 structural conformations. The green-dotted line indicates 5% deviation from the ensemble with 99,000 conformations. d Histograms of different ensemble sizes showing the distribution of predicted sPRE values