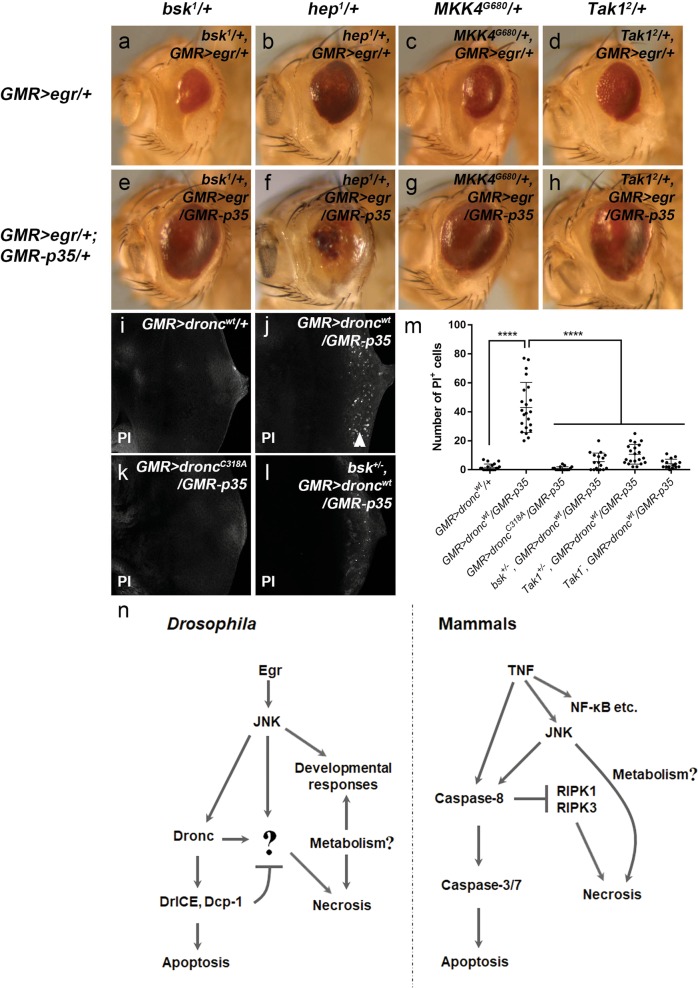
Fig. 7. JNK signaling contributes to Eiger- and Dronc-induced necrosis when apoptosis is blocked.
a–h Adult eye images. Heterozygous mutants of bsk1 (a), hep1 (b), MKK4G680 (c) and Tak12 (d) can only weakly or moderately inhibit GMR > egr-induced eye ablation phenotype (compared with Fig. 2b). In contrast, GMR > egr/GMR-p35-induced small eyes are strongly suppressed by heterozygous mutants of bsk1(e), MKK4G680 (g) and Tak12 (h), but not hep1(f) (compared with Fig. 4d). i–l Late 3rd instar larval eye disks labeled with Propidium Iodide (PI). Compared with expression of a wild-type form of Dronc (GMR > droncwt/+, i), co-expression of Dronc and P35 (GMR > dronc/GMR-p35) induces PI-positive necrosis (arrowhead, j). In contrast, PI-labeling is not observed when a catalytic site-mutated form of Dronc is expressed instead (GMR > droncC318A/GMR-p35, k). Loss of one copy of bsk (bsk+/−) strongly suppresses necrosis induced in GMR > droncwt/GMR-p35 (l). m Quantification of PI-positive cell numbers in late 3rd instar larval eye disks of various genetic backgrounds as indicated. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test was used to compute p-values. Asterisks indicate statistically significant changes (**** p< 0.0001). Loss of one copy of Tak1 (Tak1+/−) or a Tak1 null mutant (Tak1−/−) strongly suppresses necrosis induced in GMR > droncwt/GMR-p35. n A diagram showing comparable molecular mechanisms of regulated necrosis in Drosophila and mammals. The Drosophila TNF (Egr), similar to its mammalian counterparts, has multiple context-dependent functions including induction of necrosis when apoptosis is blocked. In mammals, necrosis can occur when inhibition of caspase-8 on RIPK1 and RIPK3 is removed. JNK contributes to both apoptosis and necrosis. While in Drosophila, effector caspases DrICE and Dcp-1 inhibit Egr-induced necrosis. Once this inhibition is removed, the initiator caspase Dronc can activate necrosis with an additional input(s) from JNK signaling. Key factors that mediate this necrosis downstream of caspases and JNK are currently unknown (indicated by the question mark). Moreover, energy metabolism regulators have been implicated in regulation of Egr/TNF-induced signaling responses although their exact roles remain to be determined (see “Discussion”)