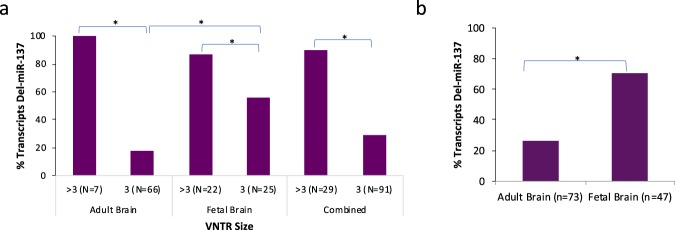
Figure 3.
VNTR Length vs. Del-miR-137 Transcript Frequency. (a) Frequency of spliced del-miR-137 transcripts are depicted for fetal, adult, and combined allele length groups. There is a significant positive association between VNTR length and del-miR-137 frequency in all three (Adult, Fetal, Combined) groups (Adult: Fishers p = 3.09e-5, Fetal: Fishers p = 0.03, Combined: Fishers p = 7.10e-9). This correlation supports a role for VNTR length in alternative pri-miR-137 splicing, and ultimately regulation of miR-137 expression. Interestingly, there is also a significant difference in del-miR-137 frequency of the 3R transcripts between developmental groups with a higher frequency of 3R transcripts spliced in the fetal group (3R Fishers p = 6.8e-4). This indicates a potential epigenetic component underlying alternative splicing and that it is neurodevelopmentally regulated. (b) The frequency of del-miR-137 transcripts was significantly higher in the Fetal group (Fishers p = 2.15e-06) compared to the Adult group. We suspect that this reflects both an epigenetic developmental difference as well as differences in VNTR lengths between groups.