Fig. 2.
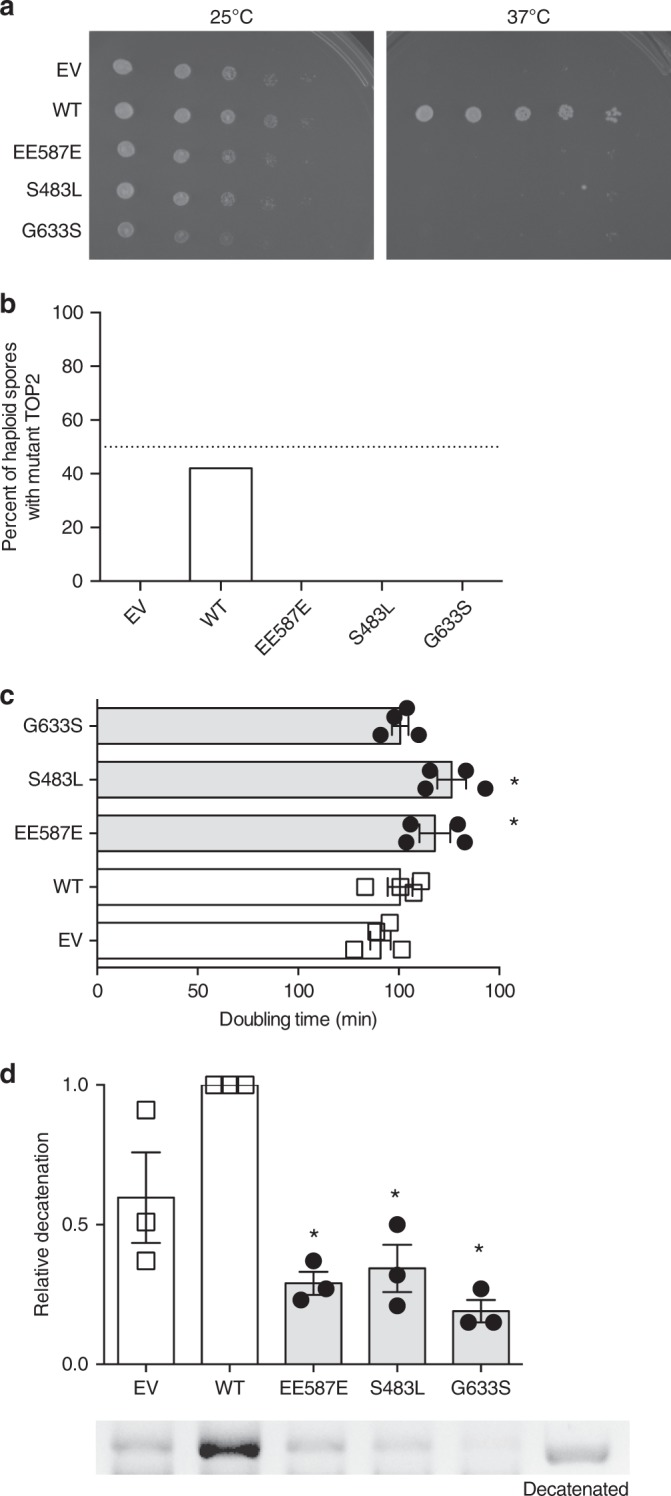
Patient mutations have a dominant negative phenotype in S. cerevisiae. a The temperature-sensitive top2–4 S. cerevisiae strain JN394t2–4 was transformed with a wild-type TOP2 vector (WT), mutant TOP2 vectors, or an empty vector (EV). Serial dilutions of transformants were spotted and incubated at 25 °C (left) or 37 °C (right). The disease-associated mutations and the empty vector were unable to complement the top2–4 mutation. Selection plates shown are representative of three experiments of independent S. cerevisiae clones. b Mutant top2 alleles were not viable. The diploid strain was sporulated, and random spores grown at 30 °C and scored for the presence of top2Δ. top2Δ spore clones were not recovered with diploids containing the empty vector and ScTOP2-EE587E, -S483L, and -G633S vectors (dotted line indicates 50%, Source data in Supplementary Table 6). c Haploid strains heterozygous for syndrome-associated TOP2 mutations (ScTOP2-EE587E and ScTOP2-S483L) have increased doubling time, whereas strains carrying ScTOP2-G633S were not as severely affected. (n = 5 independent experiments, shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). d Nuclear fractions containing Top2 isolated from haploid heterozygous strains with ScTOP2-EE587E, -S483L, and -G633S did not decatenate kinetoplast DNA as effectively as controls containing two copies of wild-type ScTOP2 or one copy of wild-type ScTOP2 and an empty vector (representative gel, Source data are provided as a Source Data file; n = 3 independent experiments, shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, Kruskall–Wallis, compared to WT)
