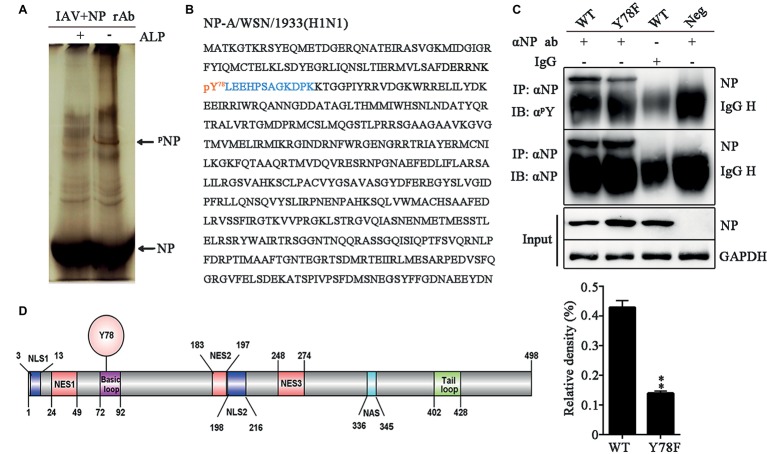
Figure 1.
NP Y78 is a conserved phosphorylation site. (A) The Phos-tag SDS-PAGE gel of phosphorylated NP immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-NP antibody. The IAV (WSN)-infected 293 T cells were lysed in lysis buffer supplemented with complete protease inhibitor cocktail and a phosphatase inhibitor phosSTOP. The extra band in untreated cells was considered to be a phosphorylated band compared to alkaline phosphatase (ALP)-treated cells. The band was digested and subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. The locations of NP and phosphorylated NP bands (pNP) are indicated by arrows. (B) LC-MS/MS analysis of the phosphorylated band. The band was identified as the IAV NP. The identified polypeptide sequence is indicated in blue, and the phosphorylated tyrosine site is indicated in red. (C) Detection of tyrosine-phosphorylated NP. A549 cells infected with viruses (WT or Y78F WSN, MOI = 1) were lysed at 12 h.p.i. and then were incubated with NP antibody and protein G agarose beads. The uninfected cells immunoprecipitated with anti-NP antibody and the infected cells immunoprecipitated with non-specific IgG served as controls. The immunoprecipitated NPs of the WT and Y78F WSN viruses were detected using anti-NP antibody (αNP) or anti-p-Tyr antibody (αpY) (top). The relative density of phosphorylated NP was normalized to total NP (below). Data are shown as mean + SD (n = 3). Difference between WT and Y78F mutant viruses was tested using unpaired Student’s t-test. **p < 0.01. (D) Schematic diagram of NP functional domains, including Y78, nuclear localization sequence (NLS), nuclear export sequence (NES), nuclear aggregation sequence (NAS), basic loop and tail loop region.