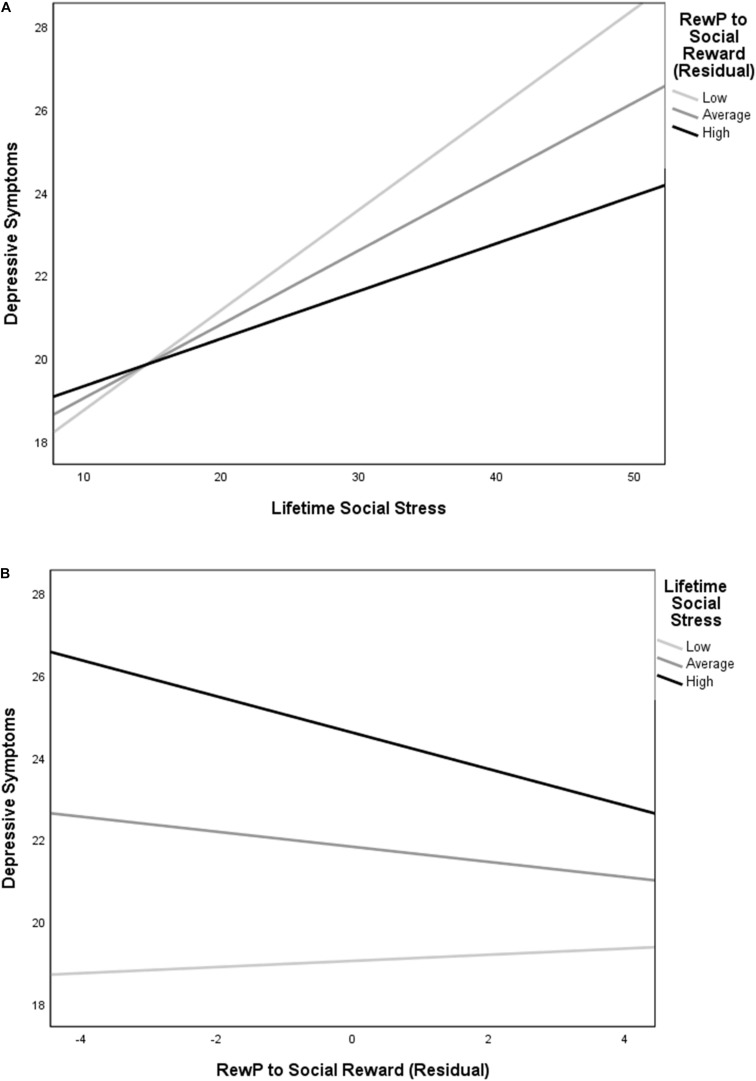
FIGURE 2.
Simple slopes depicting (A) the relationship between social stress exposure and depression at low (-1 SD), mean, and high (+1 SD) residual RewP to social reward, and (B) the relationship between residual RewP to social reward and depression at low (-1 SD), mean, and high (+1 SD) social stress. Lifetime social stress exposure was positively associated with symptoms of depression at all levels of RewP, but with a relatively stronger magnitude of association at low compared to mean and high levels of residual RewP. Reduced RewP residual predicted more depressive symptoms only at a high level of social stress.