FIG 4.
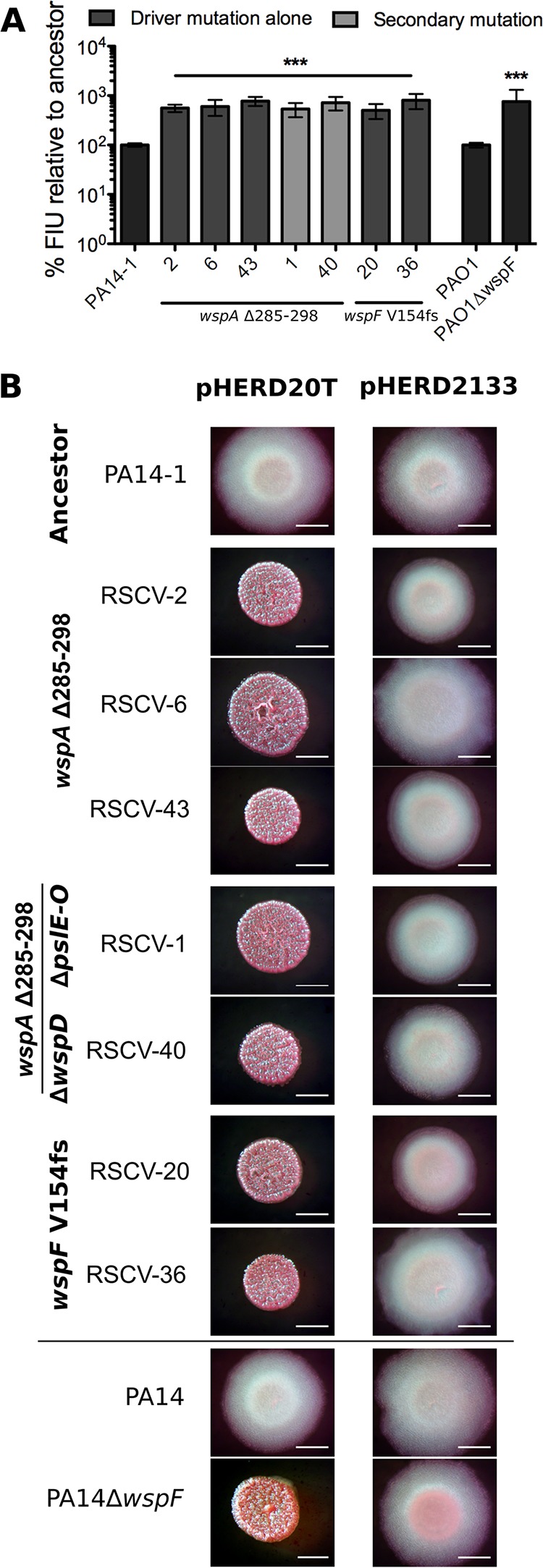
PA14-1 RSCVs have elevated intracellular levels of c-di-GMP which are responsible for the RSCV phenotype. (A) Green fluorescence was measured in representative RSCVs with the c-di-GMP reporter plasmid pCdrA::gfp. Increased GFP signal correlates to increased intracellular c-di-GMP levels. Fluorescence intensity units (FIU) of RSCVs were determined relative to the ancestor strain, which was set at 100%. PAO1ΔwspF and its isogenic parent PAO1 were used as controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA: ***, P value of <0.001 compared to the ancestor strain. (B) Colony morphology of representative RSCVs grown on VBMM plus 0.1% arabinose. pHERD20T is the empty vector. pHERD2133 has the PDE PA2133 cloned under an arabinose-inducible promoter. PA14ΔwspF and its isogenic parent, PA14, were used as controls. For both assays, representative RSCVs were selected. wspA mutants from each time point, RSCV-2, RSCV-6, and RSCV-43, were selected. Representative wspA mutants with secondary mutations were selected. RSCV-1 has the remaining psl operon deleted, and RSCV-40 has the additional wspD mutations. Representative wspF mutants, RSCV-20 and RSCV-36, were also selected. Bars, 2 mm.
