Figure 2.
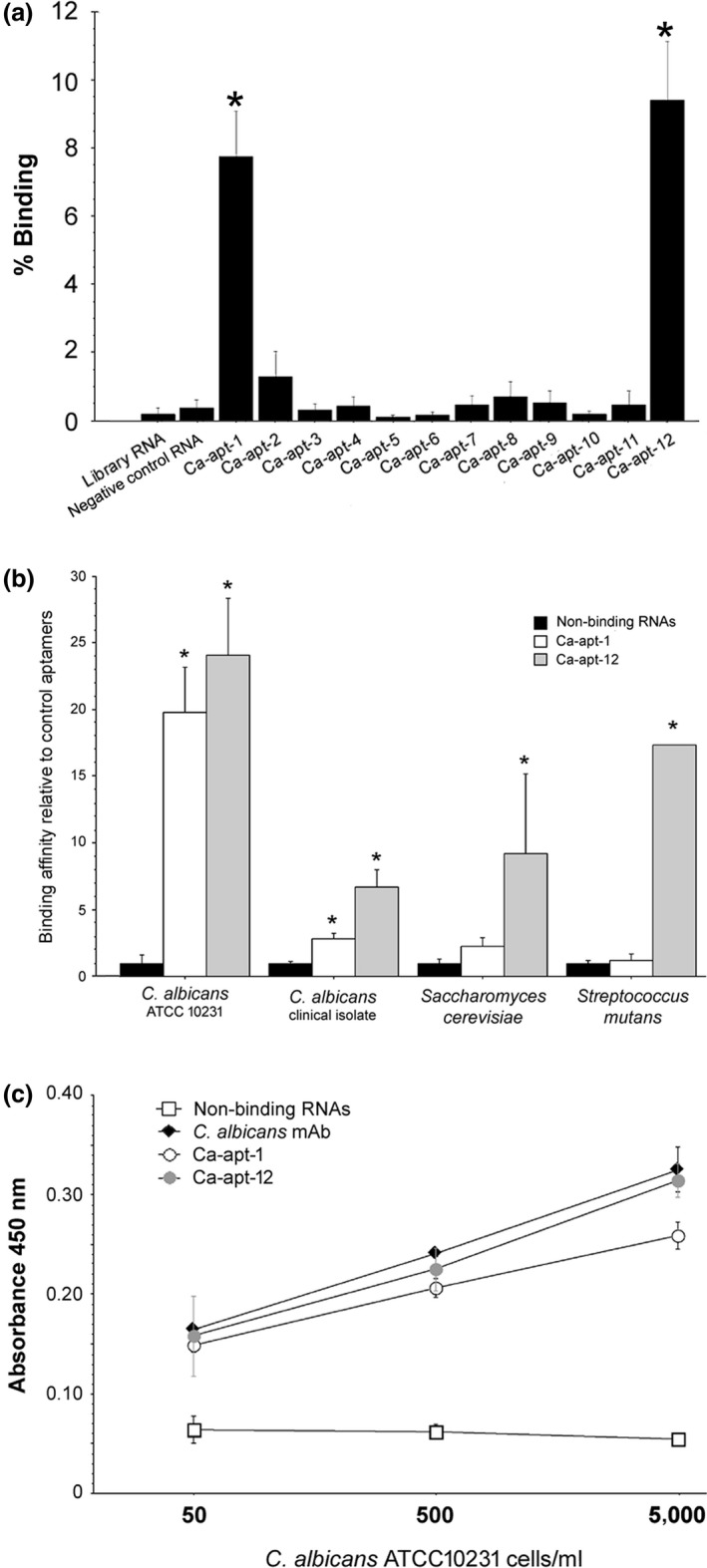
The binding properties of the Candida albicans‐specific aptamers. (a) The aptamers were screened for their binding to the C. albicans ATCC 10231 strain, which was used as the selection target. The plot shows the binding percentage (bound RNA × 100/input RNA). Only Ca‐apt‐1 and Ca‐apt‐12 demonstrated significantly higher binding than the negative control RNA. (b) The specificity of Ca‐apt‐1 and Ca‐apt‐12 was tested using either the target C. albicans strain or a clinical strain isolated from the oral cavity, a related yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Streptococcus mutans. The aptamer‐linked immobilized sorbent assay (ALISA) using both aptamers is shown and compared with an ELISA using antibodies against C. albicans. The plots show the mean values, and an error bar represents the standard error of the mean (SEM). An asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference compared with the nonbinding RNAs using an unpaired t test (p < 0.05)
