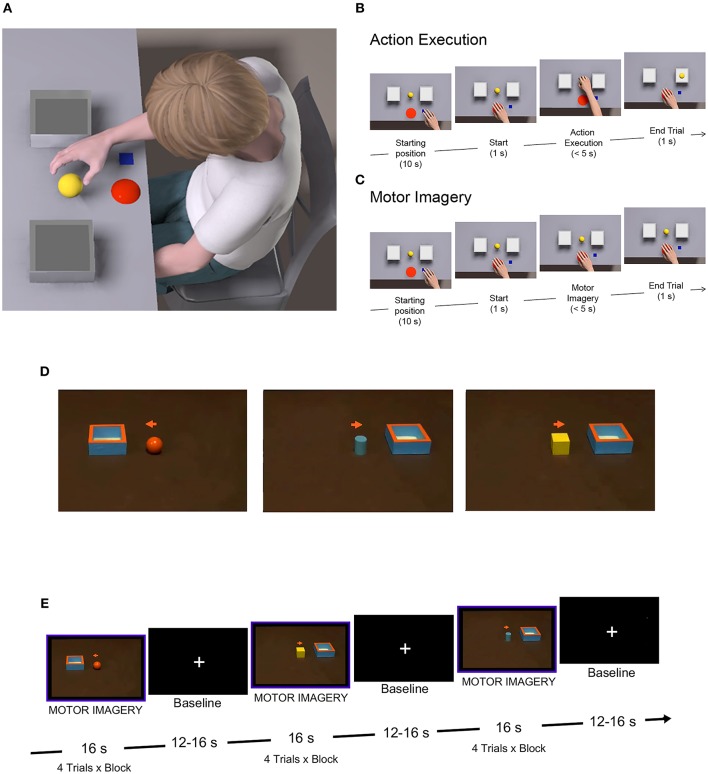
Figure 1.
Behavioral and fMRI paradigms. (A) Experimental setting for the mental chronometry task. (B) Action execution trial, consisting in reaching/grasping the object, placed at one of the three different distances with the preferred hand or the non-preferred one in different trials, and placing it into a container. (C) Motor imagery trial, requiring participants to imagine performing the same action as in (B), from a first-person perspective. (D) Stimuli used during the fMRI task, showing an object and a box on a table. Simultaneously, participants had to imagine themselves grasping the object with the non-preferred hand and placing it into the box. (E) fMRI block design, alternating task and rest conditions, with a total number of eight blocks, constituted by four trials per block.