Figure 1.
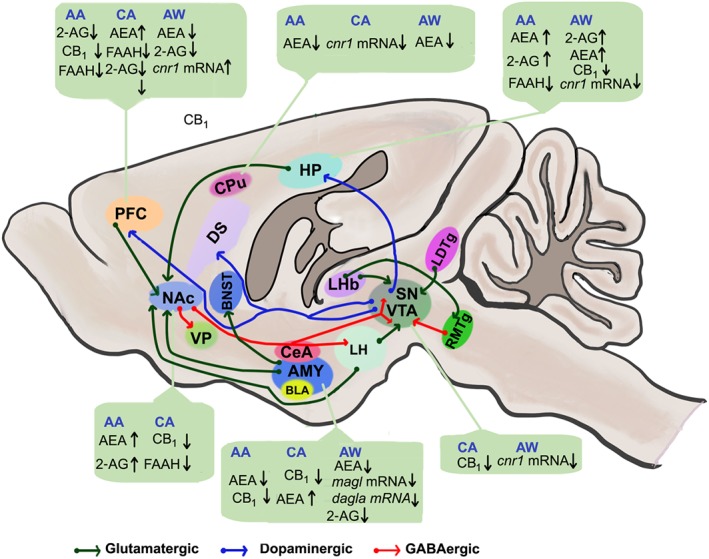
Representative sagittal cross section of a rodent brain showing the reward circuitry affected by alcohol‐induced alterations in eCB functions and highlighting signalling to and from the nucleus accumbens (NAc) and ventral tegmental area (VTA). Glutamatergic transmission drives signalling via the reward and reward‐related circuitry. GABAergic transmission from NAc and other regions suppresses neuronal activity in target regions. The release of dopamine from the VTA and substantia nigra (SN) regulates synaptic output in other target regions (dopaminergic transmission). 2‐AG, 2‐arachidonyl glycerol; AA, acute alcohol; AEA, anandamide; AMY, amygdala; AW, alcohol withdrawal; BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; CA, chronic alcohol; CB1, CB1 receptor; CeA, central nucleus of the amygdala; CPu, caudate putamen; dagla, DAG lipase‐α; DS, dorsal striatum; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; HP, hippocampus; LDTg, laterodorsal tegmentum; LHb, lateral habenula; LH, lateral hypothalamus; magl, monoacylglycerol lipase; PFC, prefrontal cortex; RMTg, rostromedial tegmental nucleus; SN, substantia nigra; VP, ventral pallidum
