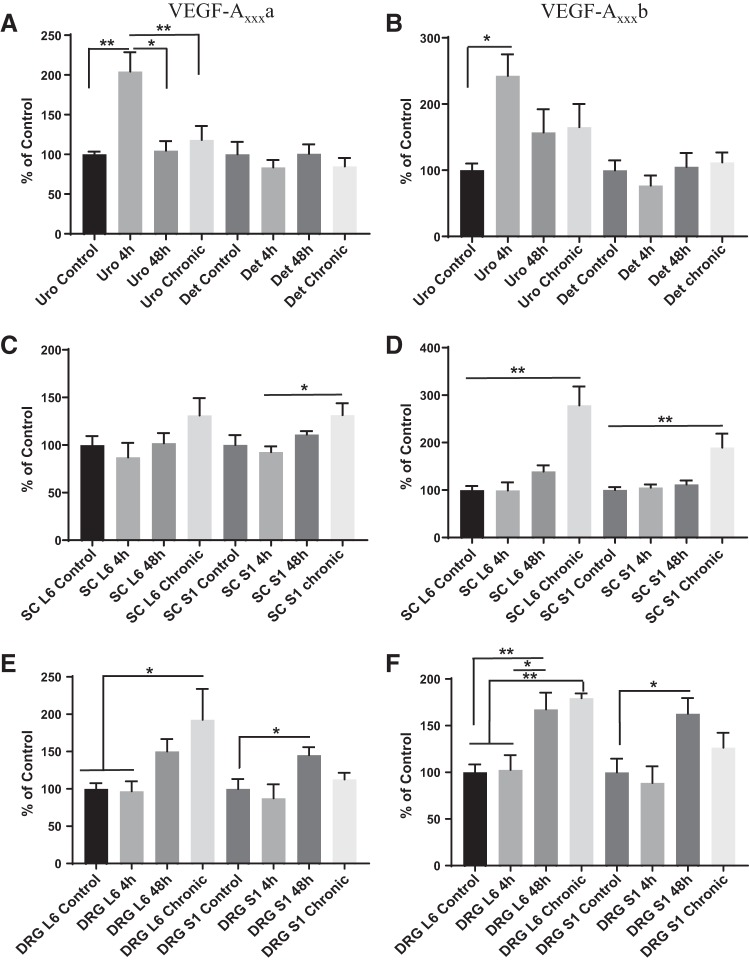
Fig. 2.
A and B: expression of VEGF-Axxxa and VEGF-Axxxb isoforms increased in the urothelium (Uro) of rats with acute (4 h) cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis (P ≤ 0.01 and P ≤ 0.05, respectively), returned to control levels after 48 h (P ≤ 0.05), and remained at control levels after 8 days (P ≤ 0.01). Det, detrusor. C and D: expression of VEGF-Axxxa was significantly greater at spinal cord (SC) level S1 after chronic CYP treatment than after 4 and 48 h of CYP treatment (P ≤ 0.05). Expression of VEGF-Axxxb was significantly greater at spinal cord levels L6 and S1 after 8 days of CYP treatment than all other time points (P ≤ 0.01). E and F: in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) L6, VEGF-Axxxa and VEGF-Axxxb were upregulated after 8 days of CYP treatment compared with control levels and 4 h of CYP treatment (P ≤ 0.05 and P ≤ 0.01, respectively). VEGF-Axxxb was significantly increased 48 h after CYP treatment compared with control (P ≤ 0.01) and 4 h after CYP treatment (P ≤ 0.05). In DRG S1, VEGF-Axxxa and VEGF-Axxxb were upregulated significantly 48 h after CYP treatment compared with control levels (P ≤ 0.05). Values are means ± SE; n = 6. Statistical analyses were performed on raw data before transformation. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.