Fig. 1.
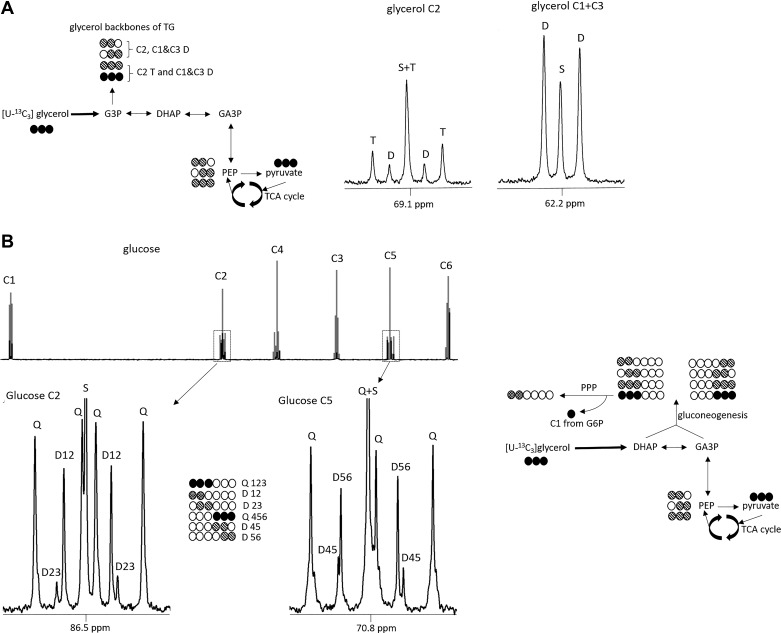
Metabolic pathways assessed by isotopomer analysis after [U-13C3]glycerol administration. De novo triglycerides (TGs) esterification pathways (A). [U-13C3]glycerol direct incorporation to fatty acid esterification leads to [U-13C3]glycerol backbones of triglycerides that are detected as a triplet in C2 region or a doublet in C1 and C3 region. Indirect pathway (transformation to pyruvate before anaplerosis to tricarboxylic (TCA) cycle and then incorporation as glycerol backbones of triglycerides) leads to the formation of double-labeled, [13C2]glycerol backbones that are detected as a doublet in C2 region. Gluconeogenesis from glycerol pathways (B). [U-13C3]glycerol direct incorporation to gluconeogenesis produces [1,2,3-13C3]- or [4,5,6-13C3]glucose that is detected as a quartet in glucose C2 or C5 region, respectively. Labeling after cycling through TCA cycle produces double-labeled glucose that can be detected in glucose C2 or C5 region. Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) leads to an increased production of double-labeled, [1,2-13C2]glucose carbon rearrangement after C1 decarboxylation from glucose-6-phosphate. C, carbon; S, singlet; D, doublet; T, triplet; Q, quartet; G3P, glucose-3-phosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GA3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate.