Figure 4.
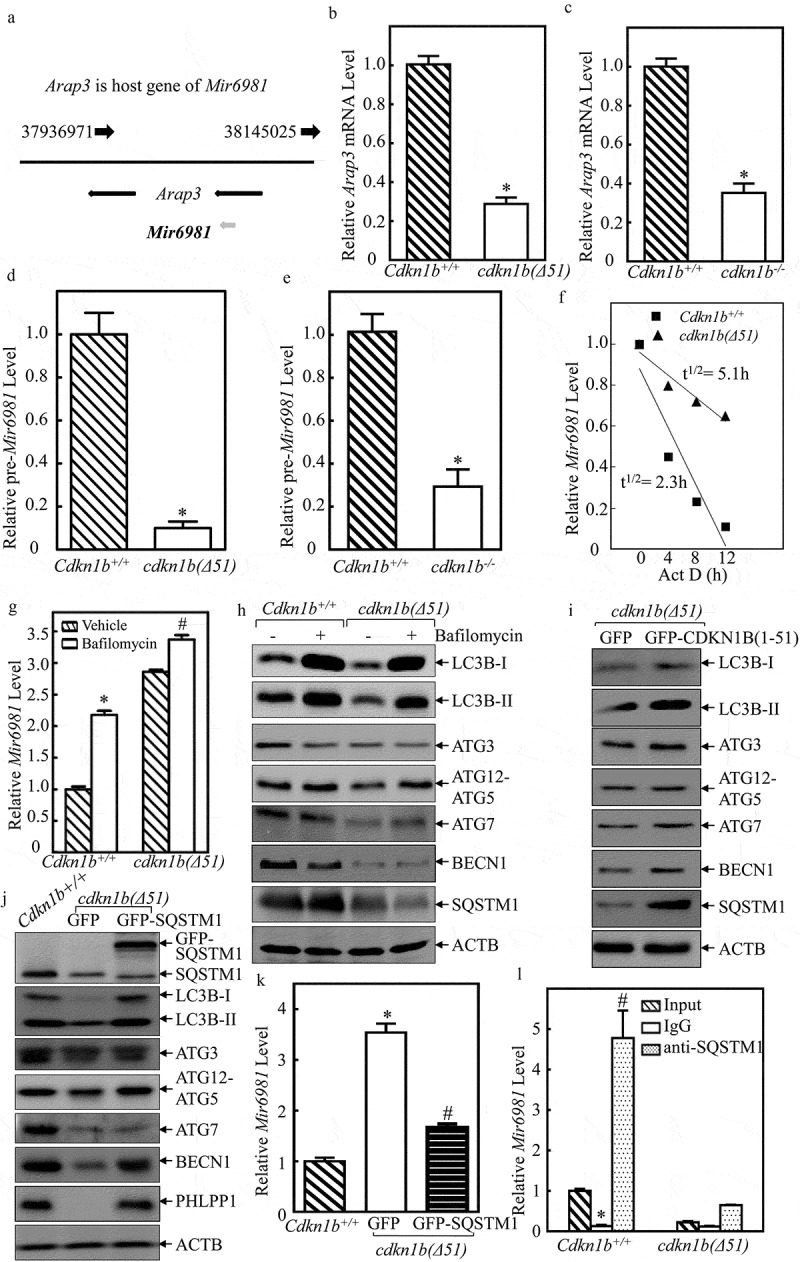
Mir6981 was degraded through a CDKN1B-mediated autophagic mechanism in SQSTM1-dependent manner. (a) The illustration of Arap3 as the host gene of Mir6981. (b,c) RT-PCR was employed to compare the mRNA levels of Arap3 in Cdkn1b+/+ vs. cdkn1b(Δ51) cells (b) and Cdkn1b+/+ vs. cdkn1b−/- cells (c), respectively. Actb was used as a loading control. (d,e) The expression levels pre-Mir6981 were evaluated by real-time PCR in Cdkn1b+/+ vs. cdkn1b(Δ51) cells (d) and Cdkn1b+/+ vs. cdkn1b−/- cells (e), respectively. The symbol (*) indicates significant inhibition (P < 0.05). (f) Mir6981 stabilities were determined by real-time PCR in the presence of actinomycin D in Cdkn1b+/+ and cdkn1b(Δ51) cells. (g) Real-time PCR was employed to evaluate the expression level of Mir6981 in Cdkn1b+/+ cells and cdkn1b(Δ51) cells in the presence or absence of BAF treatment. The symbol (*) indicates a significant increase in comparison to the vehicle control (P < 0.05). (h) Western blots were employed to evaluate the indicated protein expression in Cdkn1b+/+ cells and cdkn1b(Δ51) cells in the presence or absence of BAF treatment. (i,j) Western blots were employed to determine the indicated protein expressions in cdkn1b(Δ51) (Vector) vs. cdkn1b(Δ51)(GFP-CDKN1B) cells (i) or in Cdkn1b+/+ vs. cdkn1b(Δ51)(GFP) cells vs. cdkn1b(Δ51)(GFP-SQSTM1) cells (j). ACTB was used as a protein loading control. (k) The expression levels of Mir6981 in Cdkn1b+/+, cdkn1b(Δ51)(GFP) cells, and cdkn1b(Δ51)(GFP-SQSTM1) cells were determined by real-time PCR. (l) An RNA-IP assay was employed to evaluate the potential interaction between SQSTM1 protein and Mir6981 in Cdkn1b+/+ cells and cdkn1b(Δ51) cells. Real-time PCR was employed to determine Mir6981 levels in the immuno-complex affinity-isolation by anti-SQSTM1 antibody.
