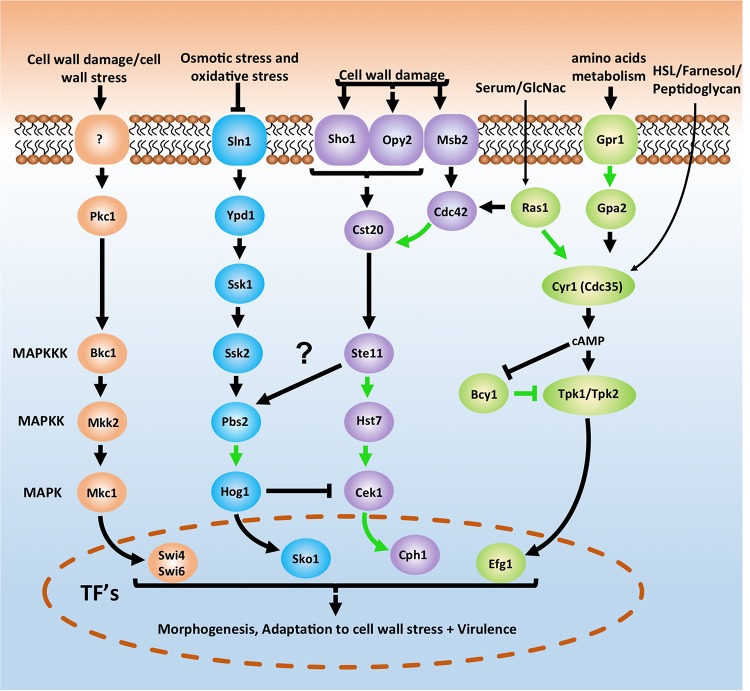
FIGURE 2.
Basic schematic representation of the cAMP-PKA pathway (green) and three MAPK pathways in Candida albicans which are important for morphogenesis, adaptation to stress and survival. The cell integrity pathway (also known as PKC pathway) is depicted in orange, the HOG pathway is shown in blue and the CEK1 mediated pathway (also known as SVG pathway) is represented in purple. Pathways depicted here are an oversimplified version. A direct interaction between Msb2 and Cst20 (van Wijlick et al., 2016) is for example not depicted here. For a more in depth overview see Refs. (Biswas et al., 2007; de Dios et al., 2010; Sudbery, 2011; Huang, 2012; Noble et al., 2017; Burch et al., 2018). Notice also the arrow between Ste11 and Pbs2. In yeast the Sho1 branch plays a role in osmotic stress signaling to Hog1 (Hohmann, 2002). However, in C. albicans this does not seem to be the case as Ssk2 is the only MAPKKK signaling to Hog1 (Cheetham et al., 2007; Román et al., 2009). Arrows in green depict physical interactions between two proteins that have already been demonstrated in C. albicans. Arrows in black are Protein-protein interactions not yet demonstrated in C. albicans. See text for more details.