Figure 2.
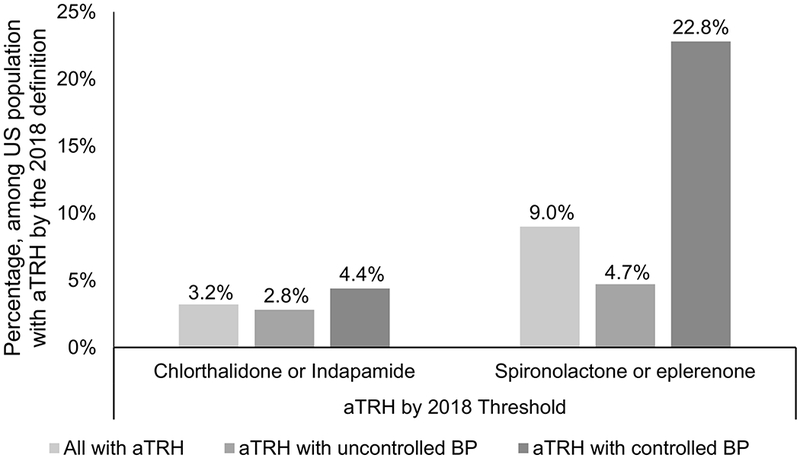
Proportion of US adults with apparent treatment resistant hypertension according to the 2018 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on resistant hypertension taking chlorthalidone or indapamide (left panel) and spironolactone or eplerenone (right panel).
aTRH: apparent treatment resistant hypertension, BP: blood pressure
According to the 2018 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on resistant hypertension, uncontrolled blood pressure was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure ≥ 80 mm Hg. For adults ≥ 65 years of age without diabetes, chronic kidney disease, history of cardiovascular disease or 10-year predicted risk ≥ 10% on the Pooled Cohort risk equations only systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mm Hg is used to defined uncontrolled blood pressure.
According to the 2018 American Heart Association Scientific Statement on resistant hypertension, controlled blood pressure was defined as systolic blood pressure <130 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure < 80 mm Hg. For adults ≥ 65 years of age without diabetes, chronic kidney disease, history of cardiovascular disease or 10-year predicted risk ≥ 10% on the Pooled Cohort risk equations, controlled blood pressure was defined as systolic blood pressure < 130 mm Hg.
