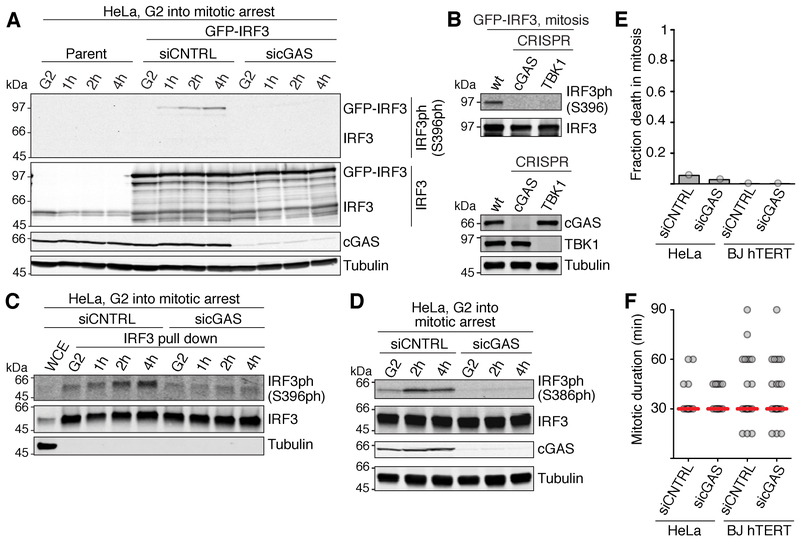
Figure 2. The cGAS pathway is inactive during normal mitosis but is activated late in mitotic arrest.
(A) Western blot analysis of IRF3 phosphorylation of the indicated HeLa cells, harvested either in G2 or after the indicated times during mitotic arrest in 500 nM taxol, 10 μM proTAME.
(B) Western blot analysis of GFP-IRF3 S396 phosphorylation in mitotic arrest using the indicated cell lines (top). Bottom, verification of CRISPR-Cas9 disruptions.
(C) Western blot analysis of S396 phosphorylation of endogenous IRF3 immunoprecipitated from G2 arrested HeLa cells, or from cells at the indicated time points during arrest in 500 nM taxol, 10 μM proTAME.
(D) Western blot analysis of IRF3 S386 phosphorylation in HeLa cells harvested either in G2 or after the indicated times during arrest in 500 nM taxol, 10 μM proTAME.
(E) Fraction of cells (determined by live microscopy) of the indicated cell line and treatment that die in an unperturbed mitosis (n=30-50 for each sample).
(F) Length of mitosis (nuclear envelope breakdown - anaphase) determined by 15 min-interval time-lapse microscopy (n=30-50 for each sample). Red line: median.
siCNTRL, non-targeting control siRNA; sicGAS, siRNA targeting cGAS.
See also Figure S2.