Figure 4.
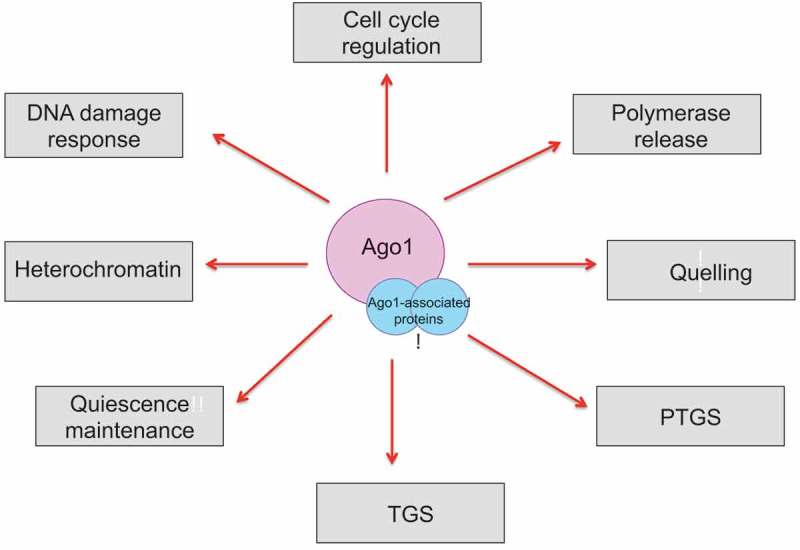
Schematic describing the various cellular roles of Argonaute and its associated proteins.
Key wordsCLRC: This cullin-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase complex consists of Clr4, Rik1, Dos1, Dos2, Stc1 and Cul4. The complex is responsible for placing the methyl marks on histone H3 lysine 9 and forming heterochromatin in the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.CTGS: Co-transcriptional gene silencing is a mechanism of nuclear RNA degradation mediated by RNAiDSBR: Double strand break repair refers to the mechanism by which cells repair DNA double-strand breaks, which are one of the most toxic lesions to a cellHR: Homologous recombination is a template-dependent DNA repair pathway implicated in the repair and tolerance of DSBs.NHEJ: Non-homologous end joining is a template-independent DNA repair pathway implicated in the repair and tolerance of DSBs.PTGS: Post-transcriptional gene silencing is a gene silencing mechanism mediated by RNAi that reduces gene expression by transcript cleavage in the absence of chromatin modificationRDRC: RNA-Directed RNA polymerase Complex consists of the RNA polymerase Rdp1, a putative RNA helicase Hrr1 and polyA polymerase Cid12. This complex catalyzes the formation of double-stranded RNA from single-stranded heterochromatic transcripts by forming phosphodiester bonds between ribonucleotides in an RNA template-dependent fashion.RITS and RISC: RNA interference transcriptional silencing complex is the effector complex of RNAi and contains the Argonaute protein bound to small RNAs. It is also called RNA-induced silencing complex in mammalian cells.RNAi: RNA interference is a silencing mechanism widely employed in eukaryotes that can be characterized by small RNAs that are bound by Argonaute effector proteins and act as specificity factors to target homologous sequences for repressionTGS: Transcriptional gene silencing is a gene silencing mechanism mediated by RNAi that triggers DNA and/or chromatin modifications that leads to transcriptional silencing and heterochromatin formation.
