Figure 1.
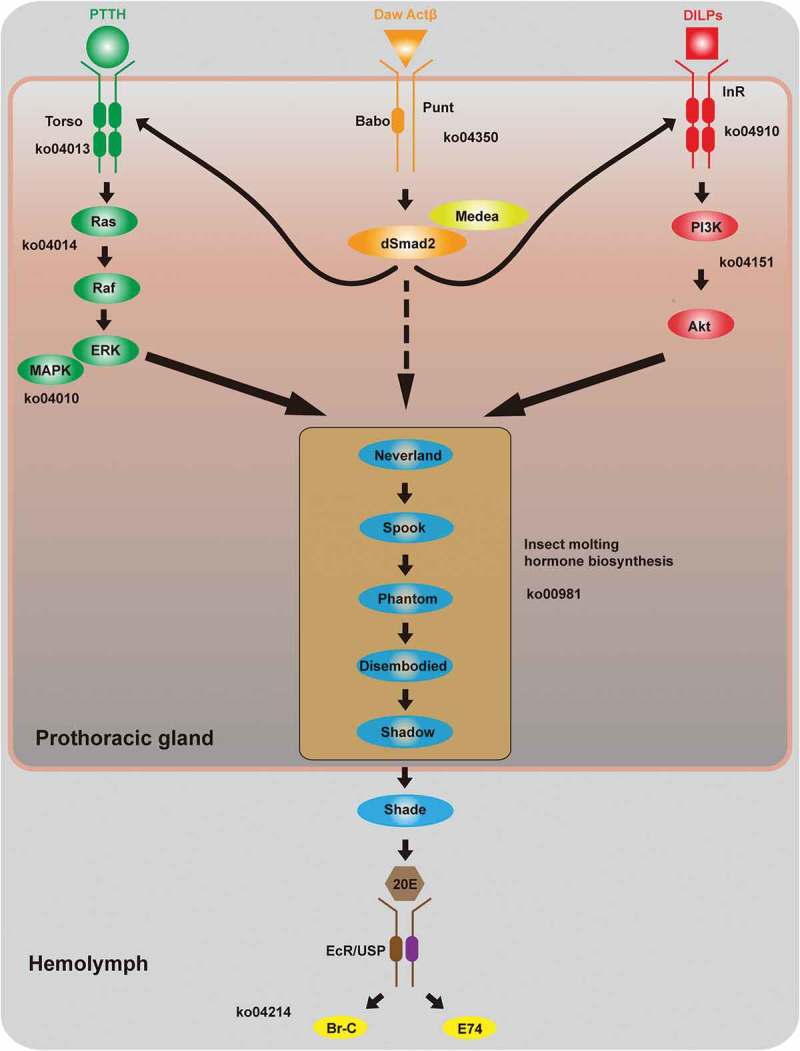
The steroid signalling network. The ecdysone-signalling network has been extensively characterized in both D. melanogaster and B. mori and contains three sections: a regulatory pathway that controls ecdysteroidogenesis, the ecdysteriod biosynthesis pathway itself, and a downstream signalling pathway that is responsive to the presence of ecdysteroids (e.g., ecdysone receptor (EcR)). Pathways in the network in B. mori include Ras signalling (KO 04014), MAPK signalling (KO 04010), TGFβ/Activin signalling (KO 04350), insulin signalling (KO 04910), Pi3k-Akt signalling (KO 04151), as well as insect hormone biosynthesis (KO 00981). The schematic illustration of the ecdysone-signalling network was modified from diagrams in three previous reports [5–7]. The hairpin structures indicate confirmed Bmo-miR-14-5p targeting in the 3ʹ UTR sequences of various genes in the network. Abbreviations: PTTH, prothoracicotropic hormone; DILPs, Drosophila insulin-like peptides; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; InR, insulin receptor; 20E, 20-hydroxyecdysone; EcR, ecdysone receptor; USP, ultra-spiracle; Br-C, broad-complex core protein.
