Figure 2.
Generation of a High-Confidence Plasmodium Protein Interaction Network
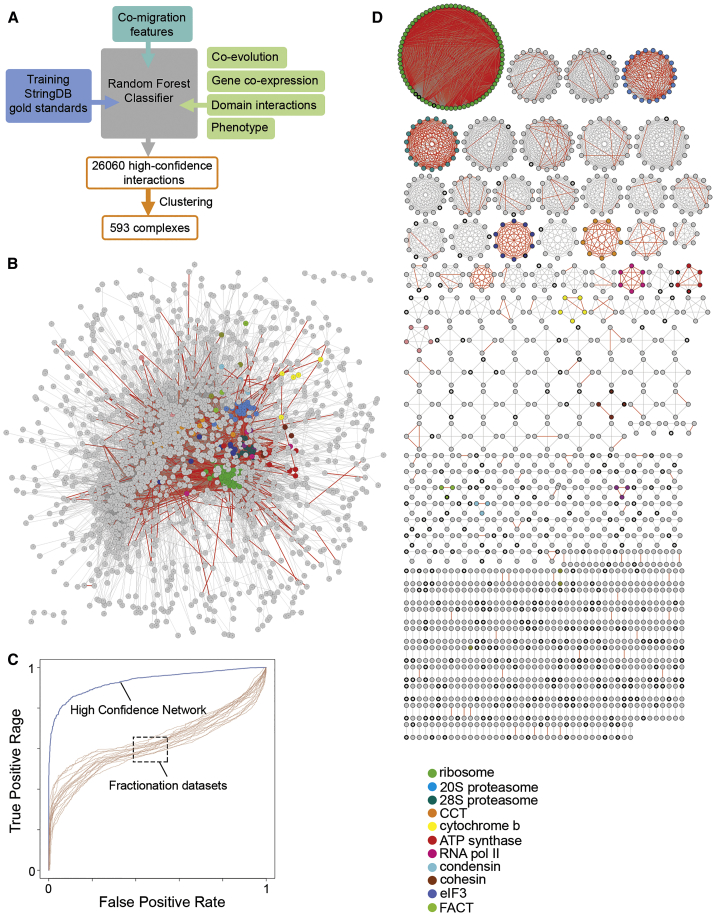
(A) Schematic of the machine learning pipeline applied to the BN-PAGE fractionation data. Pairwise co-migration scores were supported with functional association information using a random forest classifier trained with a gold standard set derived from STRING.
(B) Global Plasmodium PPI network derived through BN-PAGE correlation profiling (GBC-MS) and machine learning.
(C) Receiver operating characteristic analysis of BN-PAGE fractionation experiments (brown, mean area under the curve [AUC] = 0.63, SD = 0.023) and the random forest classifier output (blue, AUC = 0.94). Performance was assessed against a gold standard set derived from STRING.
(D) Protein clusters representing putative protein complexes. Conserved Plasmodium proteins of unknown function are shown with a thick border.
For (C) and (D), the examples of well-known complexes are colored. The red edges represent interactions annotated in STRING.