Figure 2.
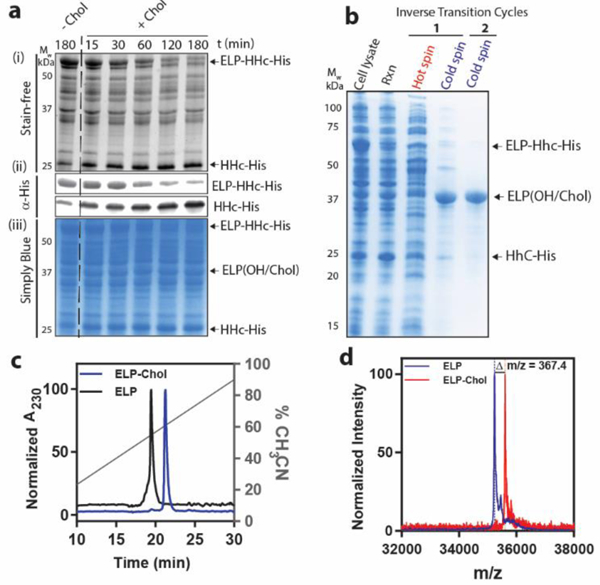
Reconstitution of cholesterolysis in E. coli cell lysate provides a facile approach to synthesize CHaMPs. a) Addition of cholesterol to cell lysate after expression of ELP-HhC-His fusion results in cleavage of the fusion protein and formation of ELP-Chol and HhC-His. Panel (i) is a SDS-PAGE gel visualized by Stain-Free technology, wherein proteins are visualized by the autofluorescence of their tryptophan residues. Panel (ii) is a western blot using anti-His primary antibody conjugated to DyLight® 550 for fluorescence visualization. Panel (iii) is a SDS PAGE gel visualized by staining with Simply Blue (a Coomassie-based dye). b) CHaMPs can be conveniently purified by exploiting their temperature-triggered LCST phase behavior using ITC. c) Reversed phase HPLC demonstrates the increased hydrophobicity of the ELP constructs after modification with cholesterol. The retention time of ELP-Chol is 19.4 min (black) while that of unmodified ELP is 21.2 min (blue). d) The MALDI-TOF MS spectrum of ELP-Chol (red) shows an increase in molecular weight compared to the ELP (blue), corresponding to the addition of a cholesterol moiety and the removal of water due to ester formation.
