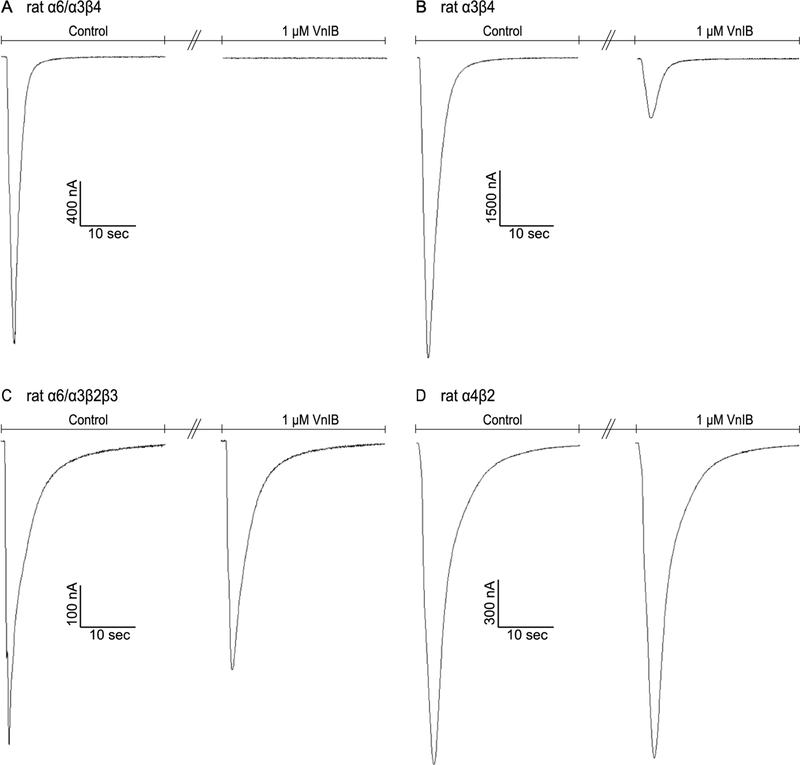
Figure 2. Comparison of α-Ctx VnIB antagonism on the signaling through various nAChR subtypes.
TEVC electrophysiology traces from individual representative Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing the α6/α3β4, α3β4, α6/α3β2β3 and α4β2 nAChRs, respectively. (A) Application of 1 μM VnIB completely abolishes the current evoked by 1 s application of 100 μM ACh at the α6/α3β4 nAChR. (B-C) Application of 1 μM VnIB partially blocks the current evoked by 1 s application of 100 μM ACh at the α3β4 nAChR (80% inhibition) and the α6/α3β2β3 nAChR (23% inhibition). (D) Application of 1 μM VnIB has no significant effect on the response evoked by 1 s application of 100 μM ACh at the α4β2 nAChR.