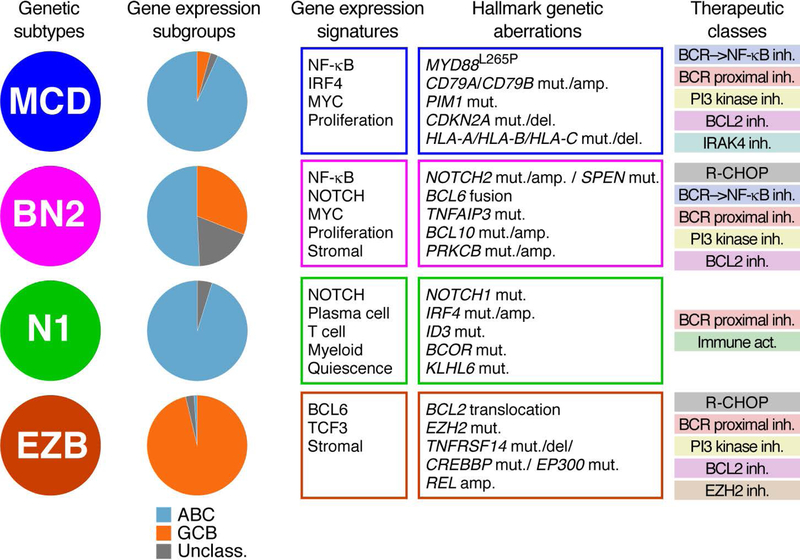
Figure 2.
Comparison of DLBCL subtypes. Relationships between genetic subtypes and gene expression subgroups (left), the gene expression signatures and associated genetic alterations (middle), as well as potential therapeutic drug classes that may have activity within these subtypes (right). Abbreviations used: inh.: drugs that inhibit the indicated targets; Immune act.: Immune activation by immune checkpoint blockade.