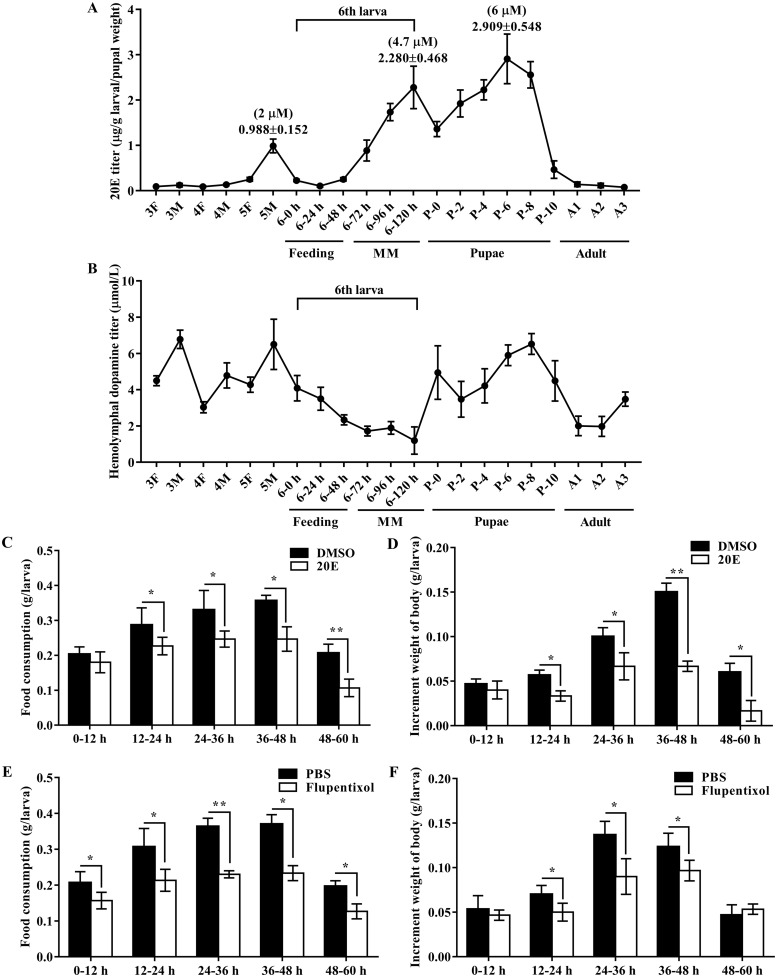
Fig 2. The 20E titer and dopamine titer in H. armigera and 20E repressed larval feeding and promoted pupation.
A. 20E titer of the whole body from 3rd instar larvae to adult 3 day (A3). B. Hemolymphal dopamine titer from 3rd instar larvae to adult 3 day (A3). 3F: third instar feeding larvae; 3M: third instar molting larvae; 4F: fourth instar feeding larvae; 4M: fourth instar molting larvae. 5F: fifth instar feeding larvae; 5M: fifth instar molting larvae; 6–0 h, 6–24 h, 6–48 h, 6–72 h, 6–96 h, and 6–120 h: sixth instar larvae from 0 h to 120 h; P0, P2, P4, P6, P8, P10: zero to 10-day-old pupae. A1-A3: adult day 1 to day 3 from female adult. MM: metamorphic molting. C. The food consumption was quantitated as the amount of diet eaten at 0–12, 12–24, 24–36, 36–48 and 48–60 h after 500 ng 20E injection. DMSO was used as control. The amount of the food consumption was weighted for the quantity of feeding. D. The increment weight of body was quantitated at 0–12, 12–24, 24–36, 36–48 and 48–60 h after 500 ng 20E injection. DMSO was used as control. E. The food consumption was quantitated as the amount of diet eaten at 0–12, 12–24, 24–36, 36–48 and 48–60 h after flupentixol injection. PBS was used as control. The amount of the food consumption was weighted for the quantity of feeding. F. The increment weight of body was quantitated at 0–12, 12–24, 24–36, 36–48 and 48–60 h after flupentixol injection. PBS was used as control. Error bars show the mean ± SD of three biological repeats. Significant differences were calculated by Student’s t test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).