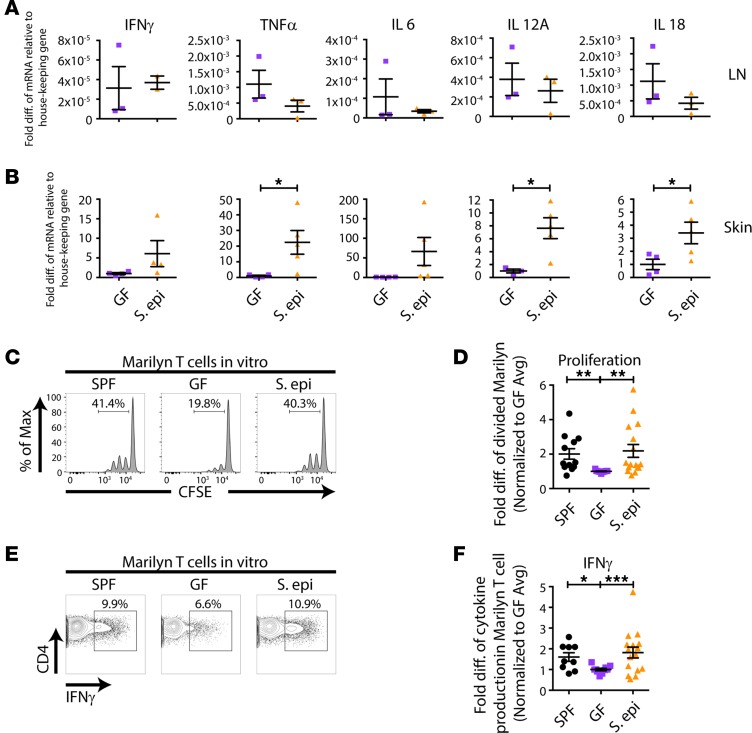
Figure 5. Skin S.
epidermidiscolonization enhances skin APC activation of alloreactive T cells. (A and B) GF or S. epidermidis–colonized skin-draining LNs (A) and skin grafts (B) were isolated on day 10 after transplantation of male skin onto female recipients, cDNA was prepared, and qPCR for cytokines was performed. Pooled results from 2 independent experiments are shown for the skin graft, normalized to GF average values. (C–F) Skin APCs were isolated from male SPF, GF, or S. epidermidis–painted GF mice and cultured with CFSE-labeled T cells from Marilyn females, followed by flow cytometric analysis. (E and F) For IFN-γ detection, cells were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin before staining. Representative plots (C and E) and quantitation of CFSE dilution of Marilyn T cells (D) and IFN-γ production by Marilyn T cells (F). Quantitation represents data normalized to the average of the percentage of divided Marilyn T cells (D) or IFN-γ production (F) in GF mice within each experiment from 2–3 experiments with n = 2–4 mice per group. Data represent the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were done using the unpaired t test (A and B) or Kruskal-Wallis test for multiple comparisons (D and F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001.