Fig. 9.
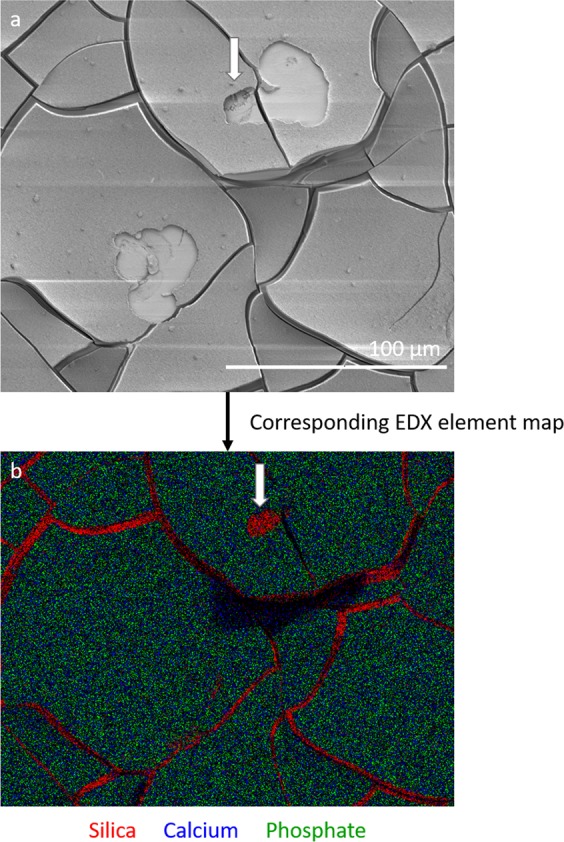
Resorption by osteoclasts did not completely remove the calcium phosphate layer on the BAG surface. a A SEM image of two resorption pits on a BAG disc surface, b the associated EDX map of the BAG disc showing silica in red, calcium in blue and phosphate in green. Silica is detected in the cracks and only in a small part of the resorption pit (white arrow). Most of the surface consisted of calcium and phosphate
