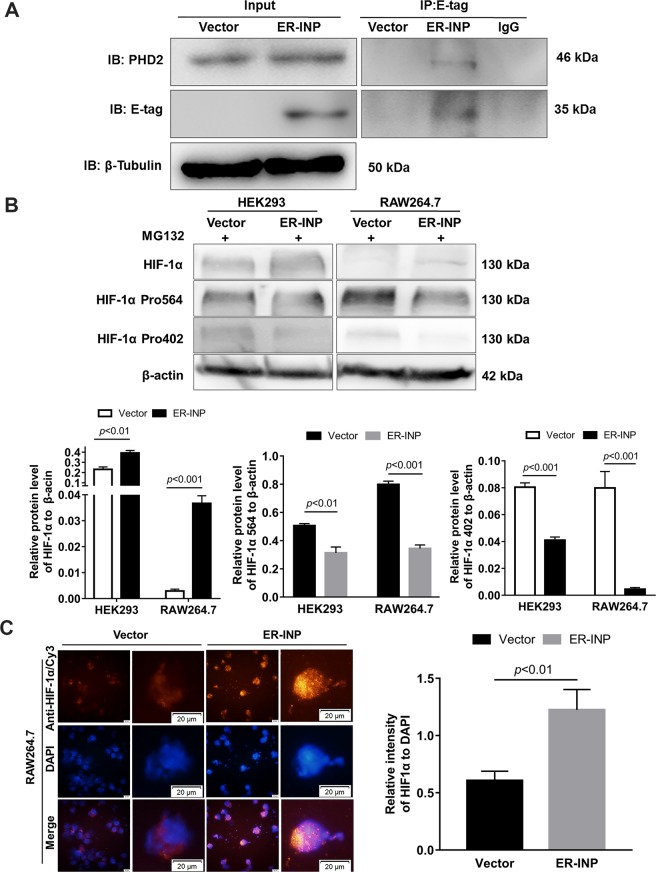
Figure 2.
ER-INP binds to PHD2, inhibits hydroxylation of HIF-1α and increases HIF-1α accumulation. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with control vector or intrabody ER-INP for 48 hours and subsequently lysed. Co-immunoprecipitation and western blot assays were performed on the cell lysis. ER-INP recognized and bound to PHD2 in HEK293 cells (n = 3). (B) Western blot analysis to measure the effect of ER-INP on HIF-1α and its hydroxylation level in transfected HEK293 and RAW264.7 cells pre-treated with MG132 (upper panel) and the protein ratio to β-actin loading control by ImageJ densitometry analysis (lower panel; n = 3). (C) Immunofluorescence assay. Expression of ER-INP increases HIF-1α accumulation in RAW264.7 cells. Cells were stained with anti-HIF-1α antibody and DAPI and then visualized and photographed under immunofluorescence microscopy (left), and mean fluorescence intensity of HIF-1α versus the mean fluorescence intensity of nuclear DAPI staining is displayed (right). Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent slides.