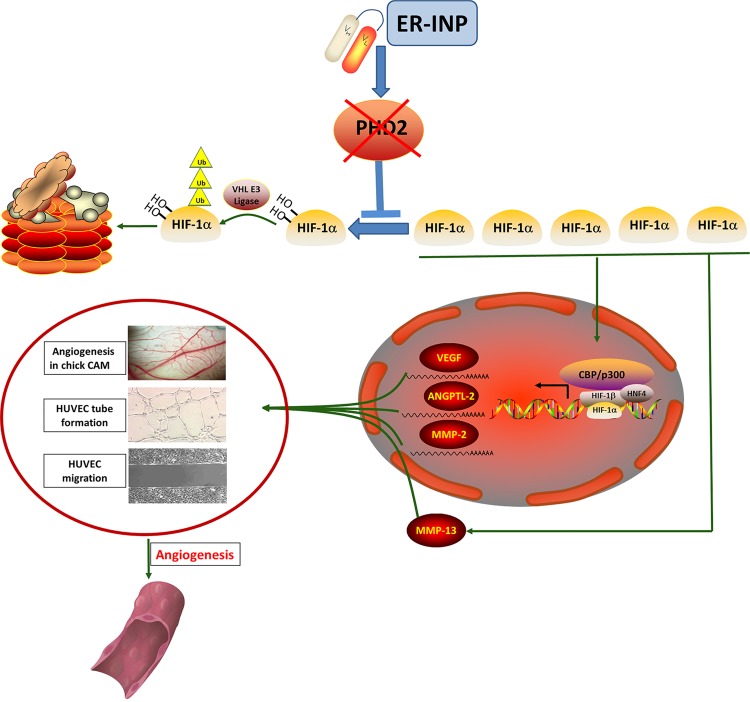
Figure 7.
Molecular mechanism of ER-INP anti-PHD2’s promotion of angiogenesis via HIF-1α stabilization and transactivation under normoxia. ER-INP intrabody binds to PHD2 and blocks PHD2 hydroxylase activity to prevent the hydroxylation, ubiquitination, and degradation of HIF-1α. HIF-1α accumulation forms dimers by binding with HIF-1β and transactivates target genes at the consensus hypoxia-responsive elements 5′-(A/G) GGTG-3′. HIF-1α target genes control numerous key cellular processes, such as angiogenesis and metabolism. HIF-1α accumulation can promote MMP-13 expression, which can also promote angiogenesis.