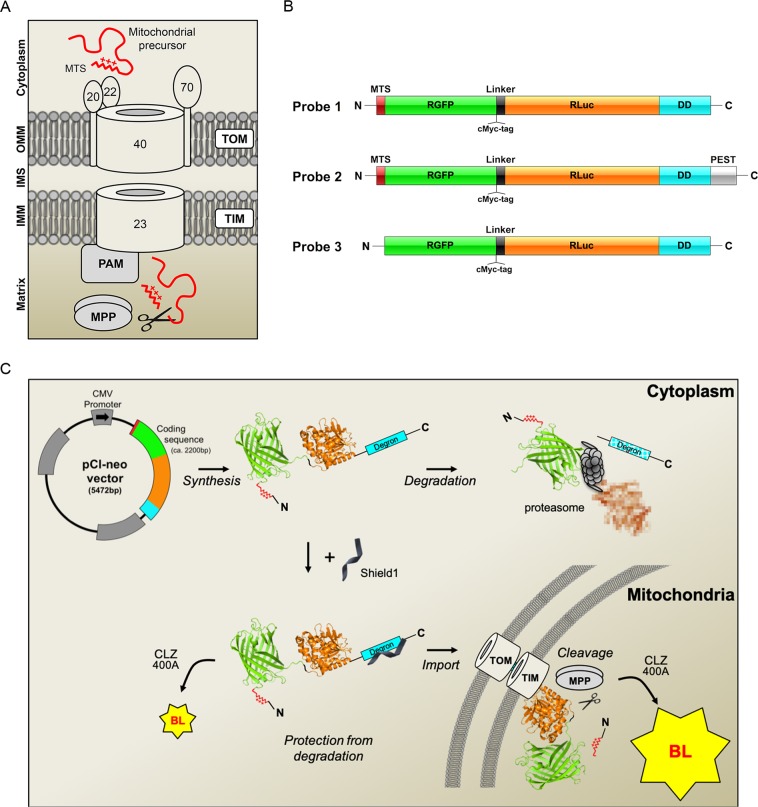
Figure 1.
Genetically encoded reporters for the assessment of protein import through the TOM complex. (A) Molecular components of the presequence import pathway: translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane (TOM) with its receptor subunits TOM20, TOM22 and the channel subunit TOM40; translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane (TIM23); presequence translocase-associated motor (PAM); mitochondrial processing peptidase (MPP). OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM inner mitochondrial membrane; IMS, intermembrane space. The TOM70 receptor recognizes proteins with internal mitochondrial targeting information. (B) Probes designed to monitor import through the presequence pathway. MTS, mitochondrial targeting signal; RGFP, green fluorescent protein from Renilla reniformis; RLuc, luciferase from Renilla reniformis; DD, destabilizing domain of FK506 binding protein (FKBP); PEST, sequence rich in proline (P), glutamic acid (E), serine (S), and threonine (T) associated with short-lived proteins; the D433A and D434A PEST mutations accelerate degradation. (C) Bioluminescence (BL)-based assay for mitochondrial import through the presequence pathway. In the absence of the small molecule Shield1, Probes 1 and 2 are rapidly degraded by the proteasome. Shield1 stabilizes the probes, which are then imported into the mitochondrial matrix through the TOM and TIM complexes. Light emission in the cytoplasm is weak, due to the presence of the MTS, blocking the N-terminus of RGFP. Cleavage of the MTS by MPP allows interaction between the RGFP and RLuc modules, leading to a characteristic light emission due to resonance energy transfer and quantum yield enhancement in the presence of the Rluc substrate coelenterazine 400A (CLZ400A). The RGFP and Rluc protein modules (PDB ID: 2RH778 and PDB ID: 2PSD78) were obtained from the Protein Data Bank79 at the following URL: http://www.rcsb.org.